FIGURE 1.
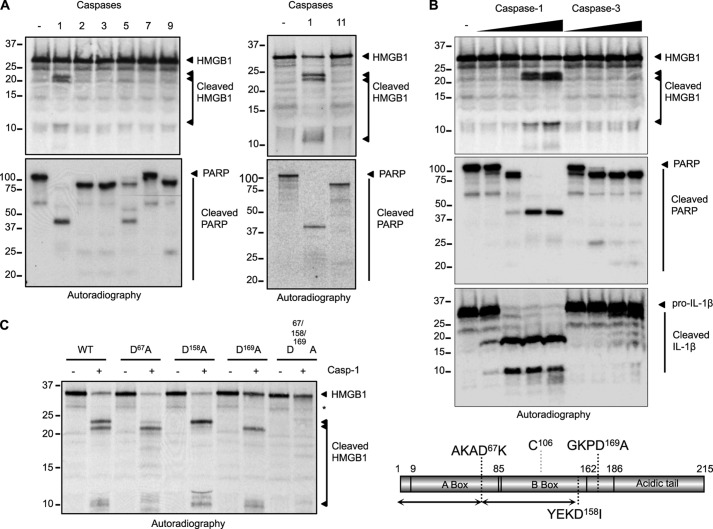
HMGB1 is a specific caspase-1 substrate. A, HMGB1 was in vitro transcribed and translated (ITT) and [35S]methionine-labeled. ITT products (1 μl) were digested with the indicated active recombinant caspases. Radiolabeled poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) was generated and treated with the same conditions to confirm the activity of the recombinant caspase preparations. The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. B, caspase-1 cleaves HMGB1 in a dose-dependent manner. Radiolabeled HMGB1 was generated as in A. ITT products (1 μl) were digested with increasing amounts of active recombinant caspase-1 or -3 and visualized by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Radiolabeled poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and pro-IL-1β were generated and treated with the same conditions to confirm the activity of the recombinant caspase preparations. C, left, site-directed mutagenesis was used to map the caspase-1 cleavage sites in HMGB1. The aspartate to alanine mutant forms of HMGB1 were tested in a caspase-1 cleavage assay using recombinant caspase-1. Right, schematic representation of HMGB1 domain organization highlighting the three cleavage sites and the redox-sensitive cysteine residue.