FIGURE 9.
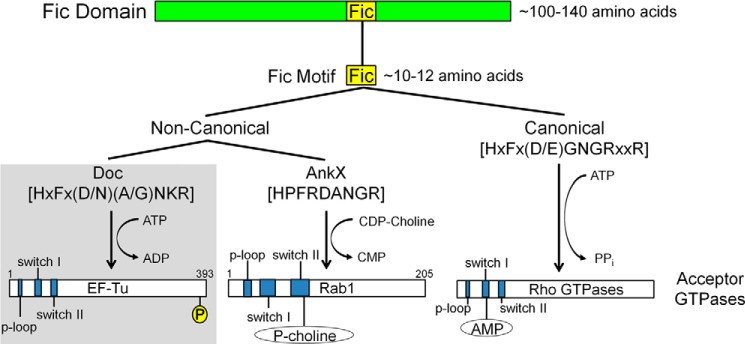
Updated overview of Fic domain proteins. Fic domain proteins are characterized by the presence of a conserved structural fold (green bar). Within this fold lies an ∼10–12-amino acid motif that is important for catalysis (yellow box). Differences in the sequence of the Fic motif allow for the designation of canonical (right branch) and noncanonical (left branch) Fic motifs. Canonical motifs are found in proteins with adenylylation activity whereas noncanonical motifs are found in proteins with other enzymatic activities. Noncanonical Fic motifs fall into two categories based on their enzymatic activities. P1 Doc (and by extension, other Doc toxins) phosphorylate GTPases at the C terminus; AnkX modifies Rab GTPase with phosphocholine. Respective Fic motif consensus sequences are bracketed. Important functional regions of the acceptor GTPases are shown in blue. P, phosphate; P-choline, phosphocholine; AMP, adenosine monophosphate. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.
