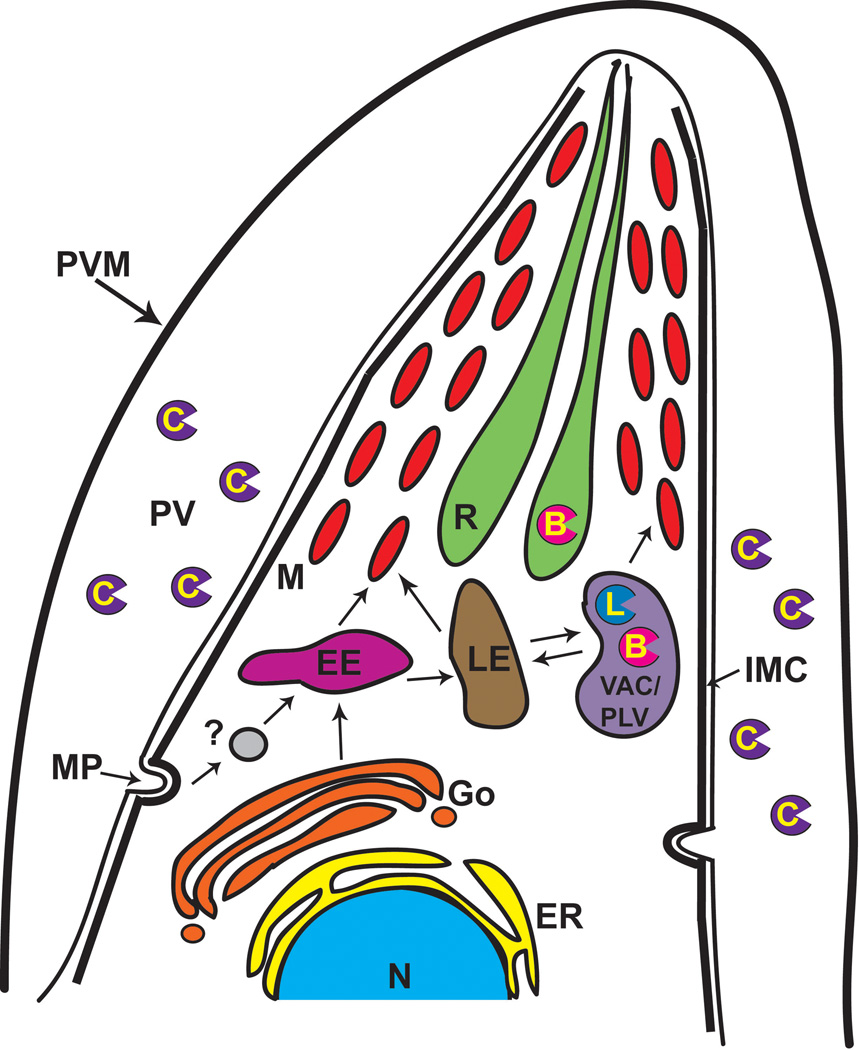
Figure 1.
The endosomal system of T. gondii and the subcellular locations of cathepsins. TgCPL and TgCPB are predominantly expressed in the VAC and a diminutive amount of TgCPL is seen in the late endosome (LE) where it has been implicated in the maturation of pro-microneme proteins.33, 34 TgCPB was also reported to be distributed in the rhoptry to function in the processing of pro-rhoptry proteins.30 Immunofluorescence microscopical studies revealed that TgCPC1 protein is secreted into the PV after cell invasion, where it may digest exogenous proteins to meet the parasite’s nutrient needs.39 Exogenous polypeptides may also be endocytosed and trafficked to the VAC for nutrient acquisition. Abbreviations used: B, cathepsin B-like protease; C, cathepsin C-like protease; EE, early endosome; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Go, Golgi apparatus; IMC, inner membrane complex; L, cathepsin-L like protease, LE, late endosome; M, microneme; MP, micropore; N, nucleus; PLV, plant-like vacuole; PV, parasitophorous vacuole; PVM, parasitophorous vacuole membrane; R, rhoptry; VAC, vacuolar compartment.