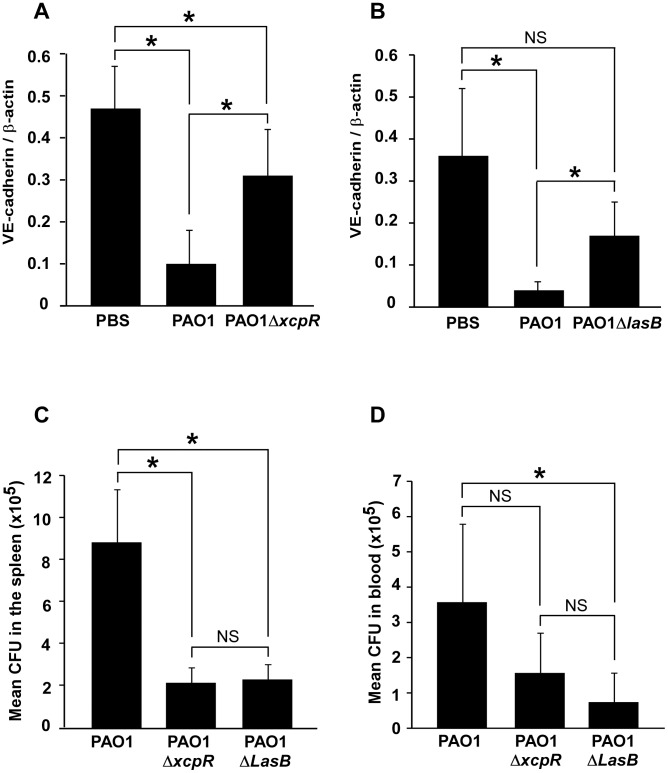
Figure 9. Decreased VE-cadherin levels in mouse acute pneumonia correlated with increased dissemination.
(A) Mice were infected by airway instillation of a suspension (2.5. 106) of PAO1, PAO1ΔxcpR or mock-infected with PBS. (B) Similar experiment with PAO1ΔLasB mutant strain. Lungs were resected 16 hours later and proteins were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against mouse VE-cadherin C-terminus (VE-cad Cter) and ß-actin (ß-act). Signals were quantified and data are presented as mean (n = 5) VE-cadherin/ß-actin signal ratios+SD. VE-cadherin levels were strikingly diminished in PAO1-infected lungs, while those infected with PAO1ΔxcpR or PAO1ΔLasB only displayed a moderate decrease. Statistics for (A): 1-way ANOVA, p<0.001, for (B): Kruskal-Wallis, p = 0.004. Pairwise significance (*) was determined by Bonferroni's test. (C, D) Mice were infected by airway instillation of a suspension of PAO1, PAO1ΔxcpR or PAO1ΔLasB (2.5. 106). Blood samples and spleen were withdrawn 16 hours later. P. aeruginosa colony forming units (CFU) were evaluated in both locations by conventional techniques. Data are presented as the mean CFU (n = 5)+SEM, calculated for total spleens (C) or total mouse blood (D). Statistics for (C): Kruskal-Wallis, p = 0.008, for (D): 1-way ANOVA, p = 0.032. Pairwise significance (*) was determined by Bonferroni's test. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.