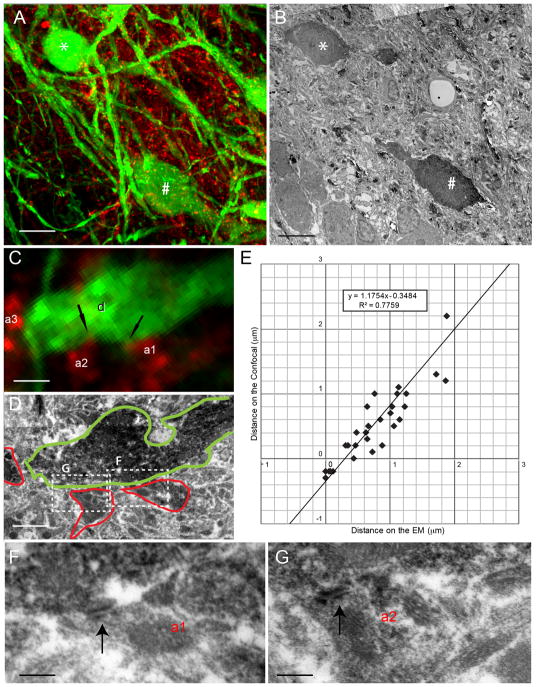
Figure 7.
Putative Synaptic Site Ultrastructural Confirmation. The confirmation of appositions was performed using high-magnification confocal microscopy combined with electron microscopy. (A) 30 μm thick sections labeled for the projection neuron cell bodies and dendrites (green) and the chorda tympani nerve (magenta) were imaged at high magnification on the confocal microscope. (B) Following antibody processing and re-sectioning as described, a 70 nm ultrathin section was visualized on the electron microscope. The cell body location and dendrite orientation provide useful landmarks for matching not only the location in the lateral plane, but also the tissue depth. Note that * and # mark corresponding cell somata in panels A and B. (C) A higher magnification view of a single optical section reveals a dendrite (d) that has overlapping pixels with two CT axon segments (a1 and a2). Nearby, there is another axonal segment (a3), which does not show apposition with the same dendrite. The examination of deconvoluted 3D stacks of this dendrite had displayed appositions at boutons that corresponded to a1 and a2, but not to a3. (D) The analogous optical plane (note that it is impossible to claim identical planes, due to indeterminable degrees of probable tilt between confocal scans and ultrathin sectioning) was located on ultrathin sections on the electron microscope. The dendrite and axon borders are marked with green and red, respectively to display degree of similarity between the confocal scan and EM sectioning planes. Although the tissue has obviously deteriorated following the intense confocal imaging and subsequent processing, a gap between a3 and d is evident. Adjacent EM sections also displayed similar gaps. (F & G) High magnification examination of ultrathin EM section illustrated in D (F) and the adjacent ones (G) revealed synapse structure (parallel arrangement of pre and postsynaptic membranes; black arrows) at the CT axon segments a1 and a2. A corresponding fluorescent overlap was also present in deeper optical planes of the confocal z-stack, confirming not only an adequate x–y resolution, but also adequate z-resolution for the identification of appositions. (E) A comparison of the distances between adjacent, near adjacent, or overlapping confocally-visualized processes with the subsequent electron microscopically measured distance reveals a strong correlation between the two (r = 0.88), confirming that the same profiles were accurately identified between the two images. The linear fit intercepts the y-axis (distances in confocal images) at −0.35 μm. This is the fluorescence diffusion factor of the confocal measurements, indicating that when there is no gap between dendritic and axonal membranes, confocal images display an overlap of 0.35 μm. Red channels were pseudocolored magenta to aid in visualization. Scale in A and B = 10 μm. Scale in C and D = 1.5 μm. Scale in F and G = 160 nm.