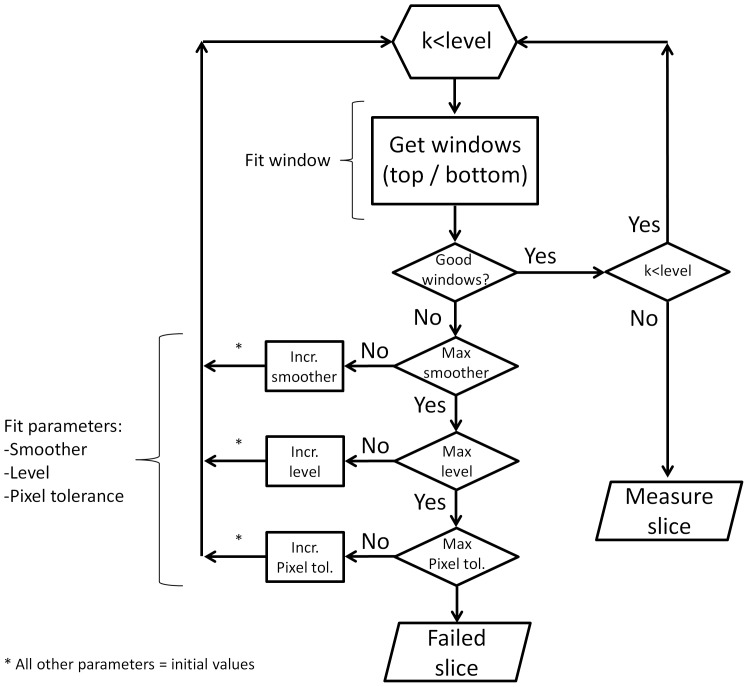
Figure 2. Flowchart describing the fitting of the different parameters.
Iterative changes are made to the values of several parameters during the running of the program. Some of these values are increased in a fixed order (smoother first, level second and pixel tolerance third) up to a maximum value, giving different iterations of the algorithm. Good detection windows are searched at each iteration by modifying the parameter window within its range of values. Given that the parameter level works by dividing the original image into narrower images, it requires some added functionality. Increasing the level from 1 to 2, for example, duplicates the number of images on which to carry out the analysis. Instead of the initial full length image, the algorithm now runs on 2 smaller images (of height equal to the original image) independently, each corresponding to the left and right halves of the initial image. The variable k is used to count which of the sub-images is being analysed.