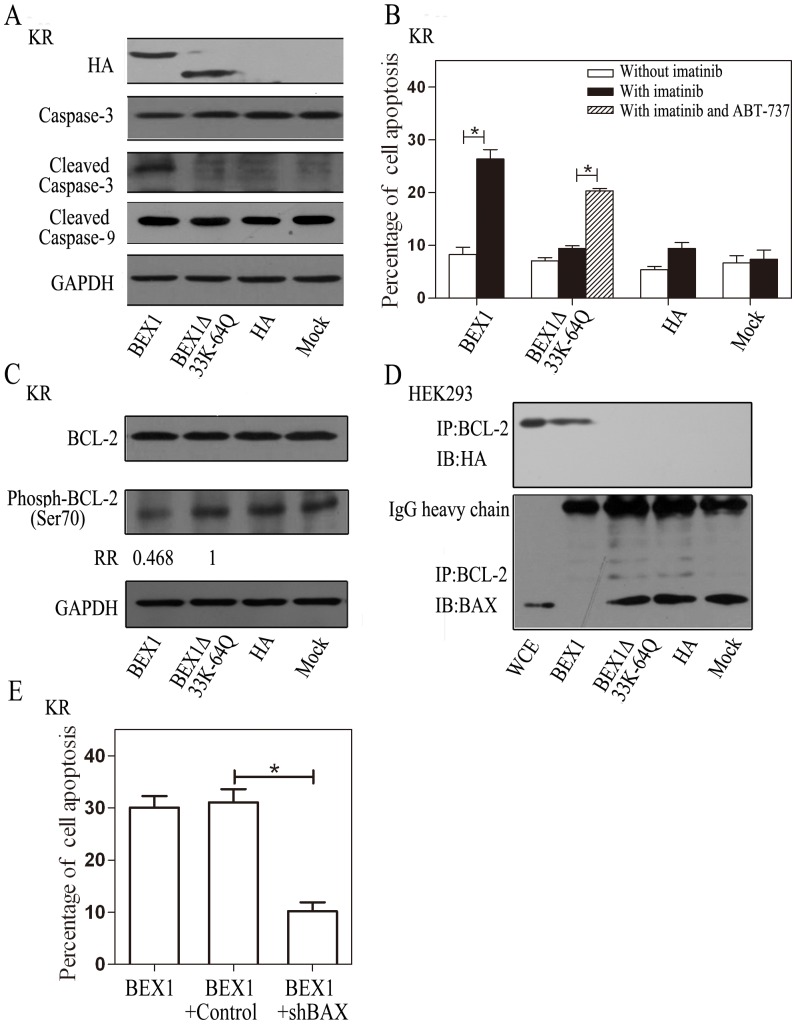
Figure 5. BEX1 promotes apoptosis by interfering with BCL-2 phosphorylation and heterodimerizing with BAX.
KR cells or HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing HA-BEX1, HA-BEX1Δ33K-64Q, empty vector control (Panel A, B, C, D), or co-transfected with HA-BEX1 and shRNA targeting BAX (shBAX) (Panel E). Forty-eight hours after transfection, 2 µM imatinib (Panel A, C and E) with or without 0.2 µM ABT-737 (Panel B) was added to the culture medium for 24 hours. A, Caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, and cleaved caspase-9 from KR cells were detected by immunoblotting analysis after the induction of apoptosis. GAPDH was used as a loading control. B, Following the induction of apoptosis, KR cells were stained with annexin V conjugated FITC and PI, and then examined by flow cytometry. Error bars represent the means ± SEM, *p<0.05. C, BCL-2, Phospho-BCL-2 (ser70), and GAPDH were analyzed by immunoblotting. Phospho-BCL-2 (ser70) bands were quantified by the Image J software and are shown as the relative ratio (RR) between HA-BEX1 and HA-BEX1Δ33K-64Q transfected cells. D, BCL-2 was immunoprecipitated with an anti-BCL-2 antibody, and the co-IP was analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody or an anti-BAX antibody. The upper bands on the anti-BAX blot were the IgG heavy chain. E, KR cells were co-transfected with the shRNA for BAX knockdown (shBAX) or the control shRNA (control) with HA-BEX1. After the induction of apoptosis, KR cells were double stained with annexin V conjugated FITC and PI as in panel B, and then examined by flow cytometry. Error bars represent the means ± SEM, *p<0.05.