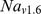Table 3. Definition and notation for the key HHM variables.
| Notation | Variable description and units | Typical value (*1 |
Potentials, in 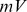 : : | ||
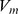
|
Membrane voltage | (*3 |
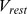
|
Membrane resting voltage | −77 |
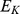
|
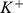 Nernst potential Nernst potential |
−90 |
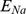
|
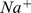 Nernst potential Nernst potential |
60.0 |
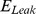
|
Leak reversal potential | −70 |
Membrane capacitance, in 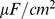 : : | ||

|
Membrane capacitance | 1 |
Maximum (*2 conductances, in 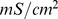 : : | ||
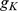
|
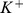 conductance conductance |
150 |
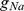
|
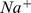 conductance conductance |
300 |
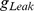
|
Leak conductance | 0.033 |
Currents, in 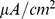 : : | ||
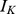
|
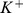 Ionic Current (*4 Ionic Current (*4
|
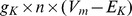
|
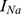
|
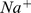 Ionic Current Ionic Current |
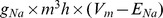
|
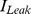
|
Leak Current |
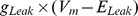
|
Notes:
(*2 These are dependent on (grow with) temperature, the values listed are for 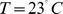 .
.
(*3 Membrane voltage is either at its resting value 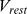 ; is depolarized (grows due to stimulation and/or activated sodium
; is depolarized (grows due to stimulation and/or activated sodium 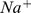 ion channels); is repolarized (decays back to
ion channels); is repolarized (decays back to 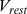 , due to the potassium
, due to the potassium 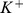 ion channels).
ion channels).
(*4 Ionic currents depend on both the membrane voltage and the dynamic state of the ion channels’ gates. See Table 4.