Abstract
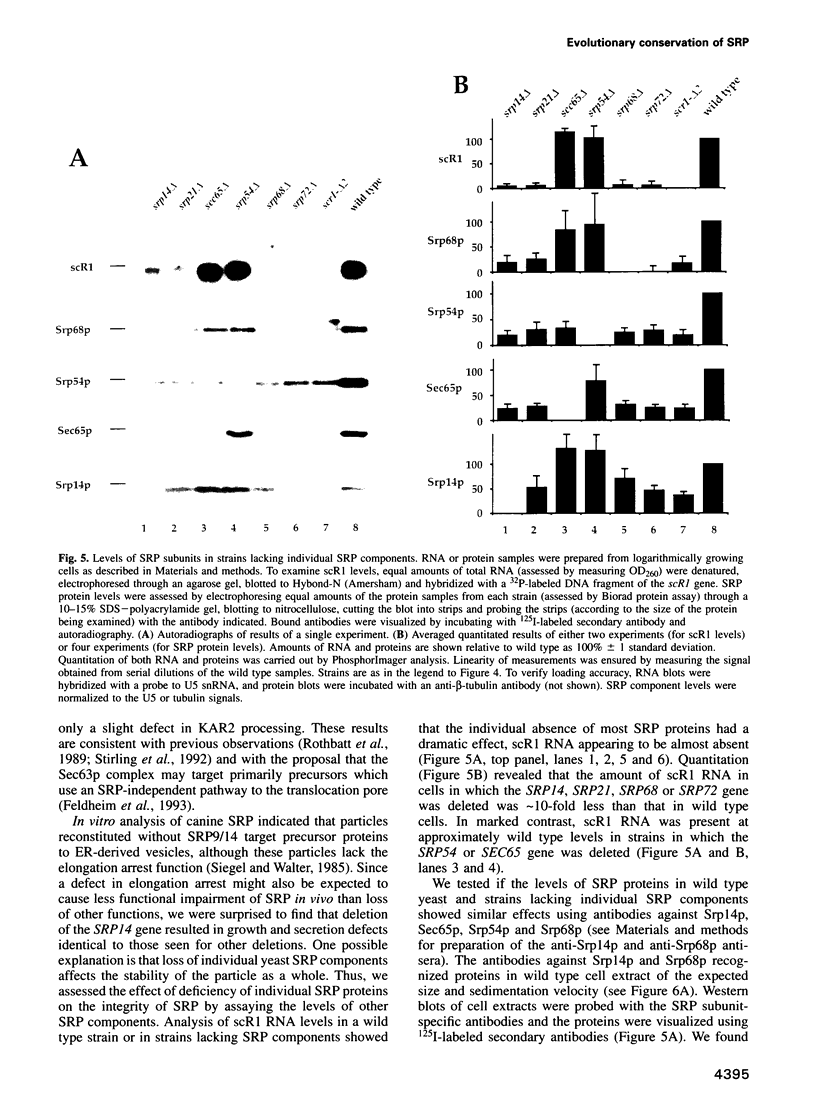
The signal recognition particle (SRP) is an evolutionarily conserved ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that functions in protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Only two protein subunits of the SRP, Srp54p and Sec65p, and the RNA subunit, scR1, were previously known in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification of yeast SRP by immunoaffinity chromatography revealed five additional proteins. Amino acid sequencing and cloning of the genes encoding four of these proteins demonstrated that the yeast SRP contains homologs (termed Srp14p, Srp68p and Srp72p) of the SRP14, SRP68 and SRP72 subunits found in mammalian SRP. The yeast SRP also contains a 21 kDa protein (termed Srp21p) that is not homologous to any protein in mammalian SRP. An additional 7 kDa protein may correspond to the mammalian SRP9. Disruption of any one of the four genes encoding the newly identified SRP proteins results in slow cell growth and inefficient protein translocation across the ER membrane. These phenotypes are indistinguishable from those resulting from the disruption of genes encoding SRP components identified previously. These data indicate that a lack of any of the analyzed SRP components results in loss of SRP function. ScR1 RNA and SRP proteins are at reduced levels in cells lacking any one of the newly identified proteins. In contrast, SRP components are present at near wild type levels and SRP subparticles are present in cells lacking either Srp54p or Sec65p. Thus Srp14p, Srp21p, Srp68p and Srp72p, but not Sec65p or Srp54p, are required for stable expression of the yeast SRP.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M., Bringmann P., Lührmann R. Purification of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles with antibodies against modified nucleosides of small nuclear RNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:232–257. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81125-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. D., Beggs J. D. Roles of PRP8 protein in the assembly of splicing complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3721–3729. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., Richard G. F., Thierry A., Dujon B. Sequence of a segment of yeast chromosome XI identifies a new mitochondrial carrier, a new member of the G protein family, and a protein with the PAAKK motif of the H1 histones. Yeast. 1992 Apr;8(4):325–336. doi: 10.1002/yea.320080410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh M., Tsay Y. F., Paulovich A. G., Woolford J. L., Jr Yeast ribosomal protein L1 is required for the stability of newly synthesized 5S rRNA and the assembly of 60S ribosomal subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2835–2845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldheim D., Yoshimura K., Admon A., Schekman R. Structural and functional characterization of Sec66p, a new subunit of the polypeptide translocation apparatus in the yeast endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Sep;4(9):931–939. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.9.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felici F., Cesareni G., Hughes J. M. The most abundant small cytoplasmic RNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae has an important function required for normal cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3260–3268. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum: a tunnel with toll booths at entry and exit. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):589–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90476-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R., Watanabe C. K., de Boer H. A. Compilation and comparison of the sequence context around the AUG startcodons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3581–3593. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Poritz M. A., Walter P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe contain a homologue to the 54-kD subunit of the signal recognition particle that in S. cerevisiae is essential for growth. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3223–3230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Stirling C. J., Walter P. SEC65 gene product is a subunit of the yeast signal recognition particle required for its integrity. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):532–533. doi: 10.1038/356532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Walter P. The signal recognition particle in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90577-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Flint N., Stanley K., Frank R., Dobberstein B. The 68 kDa protein of signal recognition particle contains a glycine-rich region also found in certain RNA-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80518-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High S., Dobberstein B. The signal sequence interacts with the methionine-rich domain of the 54-kD protein of signal recognition particle. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):229–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Sitia R. Protein degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):611–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90104-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhrer K., Domdey H. Preparation of high molecular weight RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:398–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Moon R. T. Assembly and topogenesis of the spectrin-based membrane skeleton in erythroid development. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):354–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingelbach K., Zwieb C., Webb J. R., Marshallsay C., Hoben P. J., Walter P., Dobberstein B. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding the 19 kDa protein of signal recognition particle (SRP): expression and binding to 7SL RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9431–9442. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H., Prehn S., Ashford A. J., Remus M., Frank R., Dobberstein B. Assembly of the 68- and 72-kD proteins of signal recognition particle with 7S RNA. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):977–985. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Wilhelm H., Gierasch L., Gilmore R., Walter P. GTP binding and hydrolysis by the signal recognition particle during initiation of protein translocation. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):351–354. doi: 10.1038/366351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz M., Paulovich A. G., Tsay Y. F., Woolford J. L., Jr Depletion of yeast ribosomal proteins L16 or rp59 disrupts ribosome assembly. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2261–2274. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunnari J., Walter P. Protein targeting to and translocation across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90074-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg S. C., Poritz M. A., Walter P. Signal recognition particle receptor is important for cell growth and protein secretion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Aug;3(8):895–911. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.8.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Simmons T., Shuster E. O., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Genetic analysis of small nuclear RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: viable sextuple mutant. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3150–3159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The E. coli ffh gene is necessary for viability and efficient protein export. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):744–746. doi: 10.1038/359744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Bernstein H. D., Strub K., Zopf D., Wilhelm H., Walter P. An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5S RNA resembles mammalian signal recognition particle. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1111–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1701272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld J., Capdevielle J., Guillemot J. C., Ferrara P. In-gel digestion of proteins for internal sequence analysis after one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1992 May 15;203(1):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90061-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Deshaies R. J., Sanders S. L., Daum G., Schekman R. Multiple genes are required for proper insertion of secretory proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2641–2652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Herz J., Prehn S., Frank R., Vingron M., Dobberstein B. Homology of 54K protein of signal-recognition particle, docking protein and two E. coli proteins with putative GTP-binding domains. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):478–482. doi: 10.1038/340478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Lingelbach K., Gausepohl H., Dobberstein B. The 54-kD protein of signal recognition particle contains a methionine-rich RNA binding domain. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1793–1802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger D., Brennwald P., Liao X., Wise J. A. Identification of RNA sequences and structural elements required for assembly of fission yeast SRP54 protein with signal recognition particle RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1353–1362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Binding sites of the 19-kDa and 68/72-kDa signal recognition particle (SRP) proteins on SRP RNA as determined in protein-RNA "footprinting". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Elongation arrest is not a prerequisite for secretory protein translocation across the microsomal membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1913–1921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Functional dissection of the signal recognition particle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Aug;13(8):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Hewitt E. W. The S. cerevisiae SEC65 gene encodes a component of yeast signal recognition particle with homology to human SRP19. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):534–537. doi: 10.1038/356534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Rothblatt J., Hosobuchi M., Deshaies R., Schekman R. Protein translocation mutants defective in the insertion of integral membrane proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):129–142. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Moss J., Walter P. Binding sites of the 9- and 14-kilodalton heterodimeric protein subunit of the signal recognition particle (SRP) are contained exclusively in the Alu domain of SRP RNA and contain a sequence motif that is conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3949–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Assembly of the Alu domain of the signal recognition particle (SRP): dimerization of the two protein components is required for efficient binding to SRP RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):777–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Isolation of a cDNA clone of the 14-kDa subunit of the signal recognition particle by cross-hybridization of differently primed polymerase chain reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9747–9751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Disassembly and reconstitution of signal recognition particle. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):525–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H., Luirink J., Tollervey D. Evolutionary conserved nucleotides within the E.coli 4.5S RNA are required for association with P48 in vitro and for optimal function in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):5919–5925. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D., Bernstein H. D., Johnson A. E., Walter P. The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kd protein subunit of the signal recognition particle contains an RNA binding site and can be crosslinked to a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4511–4517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]