Figure 2.
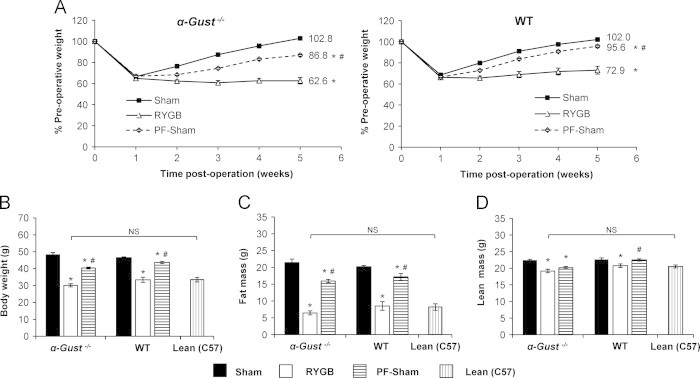
RYGB reduces body weight and improves body composition in α-Gust−/− mice. (A) Body weight, expressed as a percentage of pre-operative values, was reduced in RYGB-treated α-Gust−/− mice (left) compared to sham and PF-sham mice. RYGB induced a comparable reduction in WT mice (right). (B) Total body weight, (C) fat mass, and (D) lean mass (as measured during post-operative week 5) were reduced after RYGB in α-Gust−/− mice to levels observed in non-operated, age-matched lean C57BL/6 control mice (Lean (C57)). (n=6–11, sham; n=7–12, RYGB; n=7, PF-sham; n=7, Lean (C57)). Values are expressed as mean±SEM. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures was used to compare weight over time among surgical interventions within a genotype. One-way ANOVA was used to compare surgical interventions within a genotype. Student's t-test was used to compare RYGB-treated α-Gust−/− mice and Lean (C57) controls. ⁎P<.05 versus sham; #P<.05 versus RYGB; NS=not significant.
