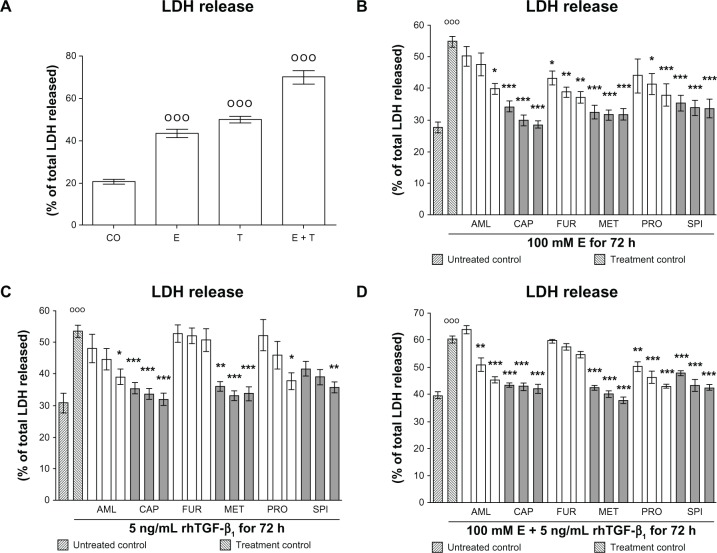
Figure 1.
Effect of antihypertensives on E- and rhTGF-β1-dependent cellular damage in hHeps. (A) LDH release of hHeps (N = 4, n = 4) treated for 72 hours with 100 mM E and/or 5 ng/mL rhTGF-β1. LDH release of hHeps (N ≥ 3, n = 4) treated with (B) 100 mM E, (C) 5 ng/mL rhTGF-β1, or (D) both substances for 72 hours in the presence or absence (treatment control) of AML (1/2/4 μM), CAP (25/50/100 μM), FUR (5/10/20 μM), MET (12.5/25/50 μM), PRO (5/10/20 μM), or SPI (12.5/25/50 μM).
Notes: DMSO was used as solvent control. Results are given as percentage of total LDH released into the culture supernatant (cells dissolved with 0.1% Triton X-100 equals 100%). Basal toxicity (untreated control) was approximately 30%. °°°P < 0.001 as compared to untreated cells; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 as compared to E- or rhTGF-β1-treated cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Abbreviations: AML, amlodipine; CAP, captopril; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; E, ethanol; FUR, furosemide; hHeps, human hepatocytes; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MET, metoprolol; PRO, propranolol; rhTGF-β1, recombinant human transforming growth factor beta 1; SPI, spironolactone.