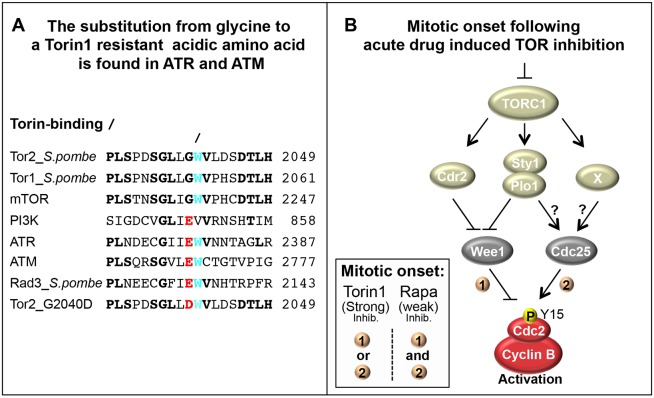
Fig. 8.
The convergence of multiple pathways to control Cdc2–cyclin-B activity. (A) Alignment of TOR and TOR-related kinases. Conserved residues are highlighted in bold. The key Torin-interacting tryptophan is shown in cyan. The Torin1 resistant tor2-G2040D is shown in red. (B) A model suggesting that when Torin1 inhibits TORC1, Wee1 levels decline. This traps Cdc2–cyclin-B in its active conformation, driving entry into mitosis at a reduced cell size. The presence of molecule X is implied by advanced mitosis in torin1-treated plo1.S402A cdr2::ura4+ double mutants. Insert: in contrast to rapamycin, regulation of either Wee1 (1) or Cdc25 (2) is sufficient to advance mitotic onset following the strong Torin1-induced TOR inhibition.