Figure 5.
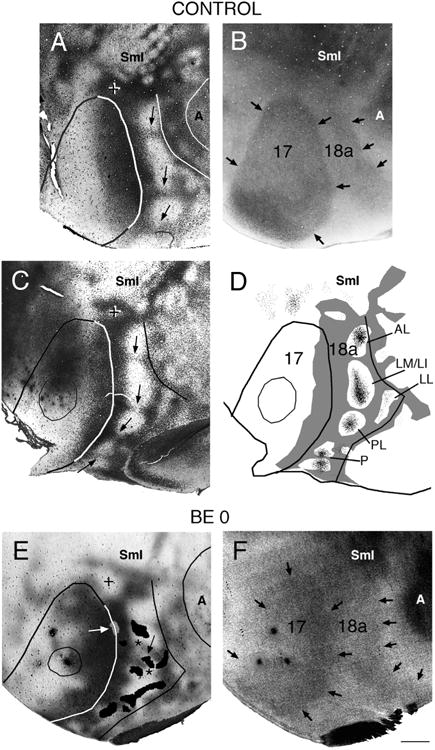
Correlating the patterns of striate–extrastriate and visual callosal connections. Lateral is to the right, anterior is up. A,B: Callosal (A) and myelin (B) patterns in normal adult rat. In A, dark areas correspond to dense accumulations of retrogradely labeled somas and anterogradely labeled axons; the profiles of areas 17, 18a, and auditory cortex were drawn following myelin boundaries in the myelin pattern (B). Arrows in A indicate callosal bridges across area 18a, which separate several acallosal ring-like regions; the cross indicates the anterior callosal ring (Olavarria and Montero, 1984); black arrows in B indicate myelin boundaries. C: Callosal pattern in normal adult rat. Arrows point to callosal bridges separating several acallosal ring-like regions in area 18a. The cross indicates the anterior callosal ring. D: Thresholded version of callosal pattern in C is shown in gray. Fine black dots in extrastriate cortex indicate anterograde transport of tritiated proline from an injection of this tracer into striate cortex (thin outline). Lateral border of area 18a is delineated by black line. (Modified from Olavarria and Montero, 1984). E: Callosal pattern revealed following multiple injections of HRP in adult rat enucleated at birth. Dark areas correspond to dense accumulations of retrogradely labeled somas and anterogradely labeled axons. The cross indicates the anterior callosal ring. Asterisks mark two interrupted callosal bridges; striate–extrastriate projections are represented as black patches in area 18a, and arrow indicates striate projection field “wedged” between the two interrupted callosal bridges. White arrow points to small projection field (gray) contained in an area of reduced callosal labeling at the 17/18a border. The profiles of areas 17, 18a, and auditory cortex were drawn from the callosal pattern in E and the myelin pattern in F. F: Myelin pattern from case shown in E. Arrows indicate borders of areas 17 and 18a. A, auditory cortex; other conventions as in Figure 4. Scale bar = 1.0 mm.
