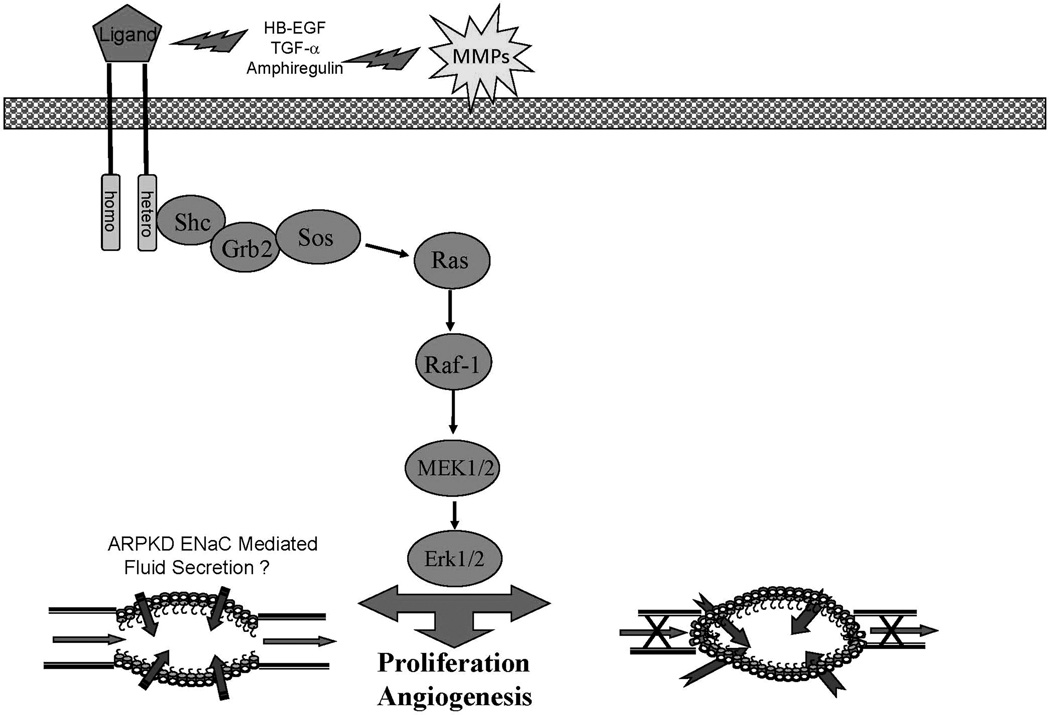
Figure 1.
An overview of the EGFR-axis pathway that contributes to cyst formation and progressive enlargement in ADPKD and ARPKD. Abnormal expression and apical localization of the EGF receptors in the presence of increased ligand availability due to increased activity of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) establishes an autocrine/paracrine cycle that drives cellular proliferation. Ligand binding leads to the formation of homodimers or heterodimers that initiates autophosphorylation and activates the MAPK pathway resulting in proliferation.