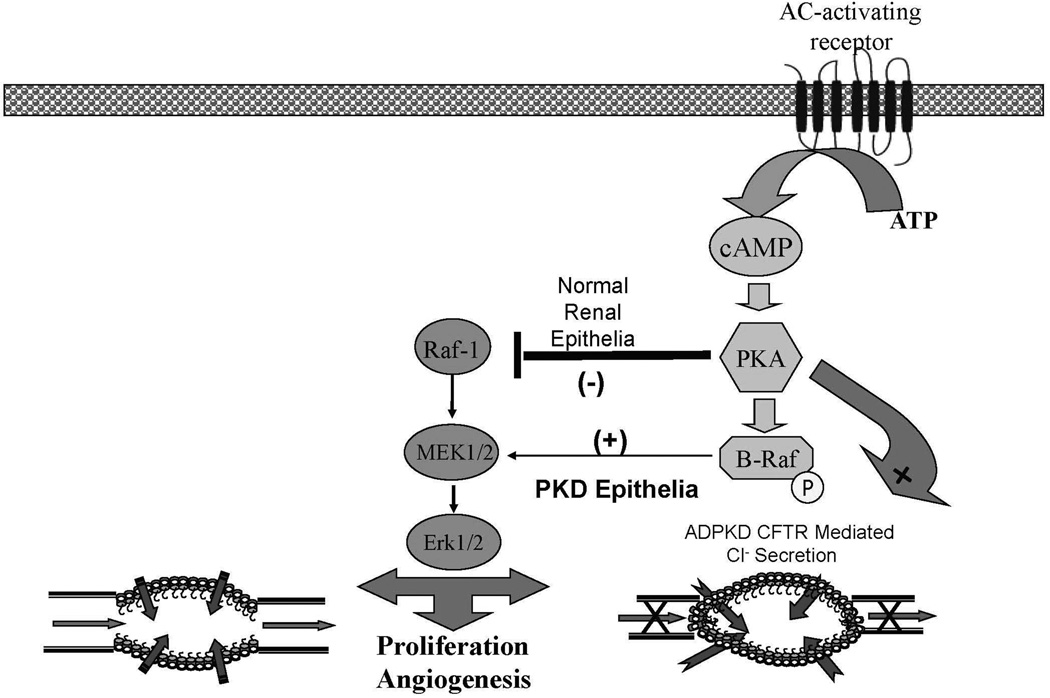
Figure 2.
A simplified representation of the cAMP or G-protein pathway that contributes to cyst formation and progressive enlargement in PKD. Adenylyl-cyclase activation leads to increased levels of cAMP which activates PKA. PKA activation in the presence of low intracellular calcium levels phosphorylates β-Raf in a Src-dependent process. This phosphorylated β-Raf allows the cell to bypass the normal inhibition of PKA on MAPK activation and leads to increased cellular proliferation and possibly angiogenesis via activation of Erk 1/2.