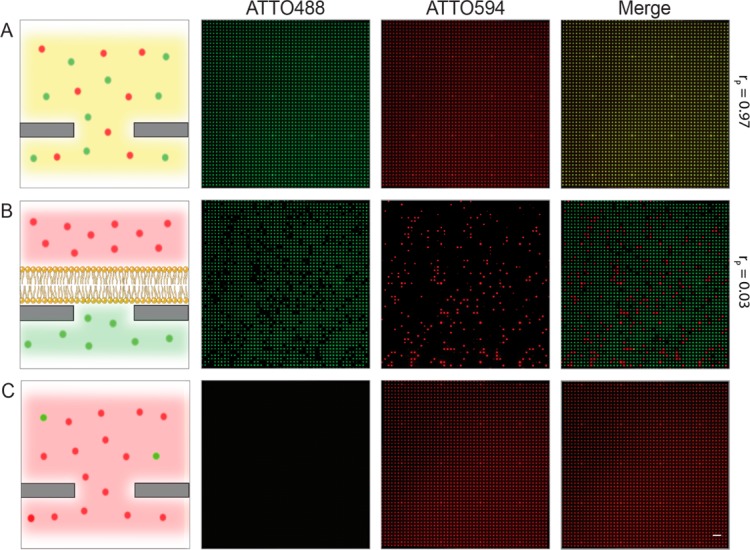
Figure 3.
Compartmentalization of solutes by nanopore SLBs. (A) Fluorophores easily access chip cavities if no SLBs are present, resulting in perfect colocalization, when, for example, two dyes are added to the buffer reservoir (ATTO488 and ATTO594; Pearson’s coefficient rP = 0.97 ± 0.01). (B) Lipid bilayers spanning the nanopores retain small hydrophilic fluorophores inside the femtoliter cavities and seal them from the buffer reservoir by an impermeable barrier. If a second fluorophore is added after SLB formation, no colocalization is observed (rP = 0.03 ± 0.02). (C) By addition of Triton X-100 (0.5% (v/w) final concentration), the SLB is disrupted, leading to efflux of ATTO488, while the external fluorophore (ATTO594) will simultaneously fill the cavity. Scale bar = 10 μm.