Figure 5.
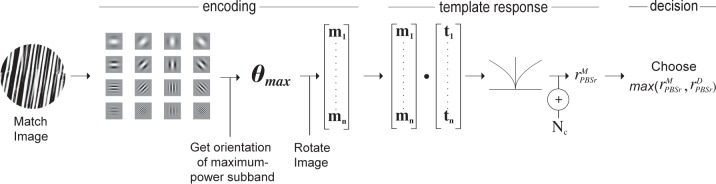
The PBSr model. Encoding phase: The image is subjected to a multiscale and multi-orientation decomposition from which it derives an estimate of the orientation of the image, θmax, relative to the target (see text). It rotates the original (nondecomposed) image so that its maximum power subband is aligned with that of the target. The vectorized, rotated, intensity-based representation (of the original, nondecomposed image), m, constitutes the search template. Template response: An intensity-based representation, t, of the target image is formed, as in the PBS model, and correlated with m. The result is rectified, passed through a power function, and corrupted by additive noise, Nc, yielding noisy scalar response value,
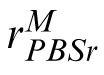 . Decision phase: The observer derives a similar response,
. Decision phase: The observer derives a similar response,
 , to the distractor and compares it to rM. The stimulus yielding the maximum response is the observer's choice for the match stimulus.
, to the distractor and compares it to rM. The stimulus yielding the maximum response is the observer's choice for the match stimulus.
