Figure 5. Effects of l-ICP on cocaine-induced hyperactivity in mice.
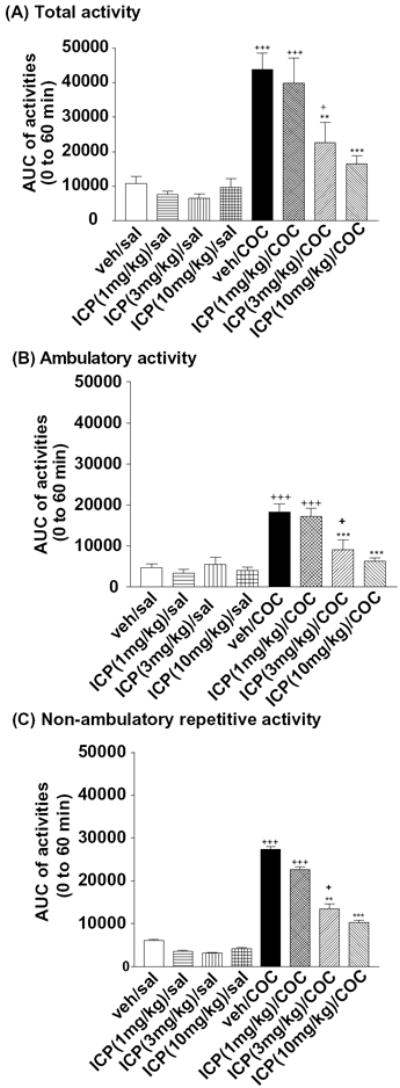
CD-1 mice were habituated to activity chambers for 50 min, pretreated with vehicle or l-ICP (1, 3 and 10 mg/kg, i.p.) for 10 min followed by saline or cocaine (20 mg/kg, i.p.) as described in Methods. Areas under curves (AUCs) were calculated for (A) total activity, (B) ambulatory activity and (C) repetitive non-ambulatory activity. Each value represents mean ± s.e.m (n=16 for veh/saline, n= 10 for all other groups).
**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, compared with the veh/cocaine group; +++P<0.001, +P<0.05 compared with veh/saline, both by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.
