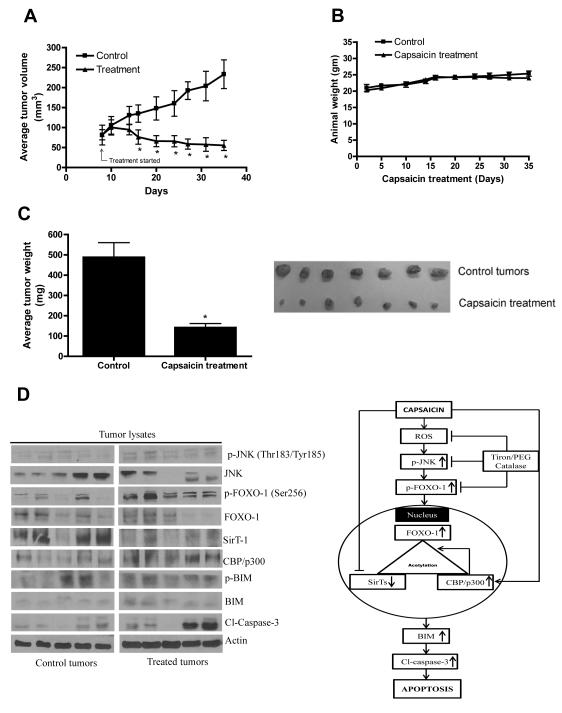
Figure 6. Capsaicin suppresses the growth of BxPC-3 human pancreatic tumor xenograft by activating JNK/FOXO/BIM cascade.
About 1×106 BxPC-3 cells were injected subcutaneously on right flanks of each athymic nude mouse in PBS/Matrigel suspension. When tumors reached 70 mm3 in size, mice were randomly divided to two groups with 10 mice in each group. Mice were fed with 5mg/kg capsaicin everyday by oral gavage. Control mice received vehicle only. Tumors were measured by vernier calipers three times a week. Each mouse was weighed twice a week. Effect of capsaicin on (A) tumor volume, (B) body weight and (C) tumor weight were evaluated. Picture of control and capsaicin treated tumors (Fig. C) Right side panel. (D) Tumor lysates from control and capsaicin treated nude mice were immunoblotted and analysed for p-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185), JNK, p-FOXO-1 (Ser256), FOXO-1, SirT-1, CBP/p300, p-BIM (Ser69), BIM, Cl-caspase-3. The blots were stripped and reprobed for actin to ensure equal protein loading. Values are means ± SEM of 10 samples. *, P<0.05 statistically significant when compared with control. Each lane of blot corresponds to the tumor sample from one mouse. Fig 6D right side panel: Tentative mechanism of action of capsaicin in pancreatic cancers cells.