Fig. 3. Phage clone 2/165 and the derivative peptides inhibited the binding of mAb UN1 to UN1-positive cancer cells.
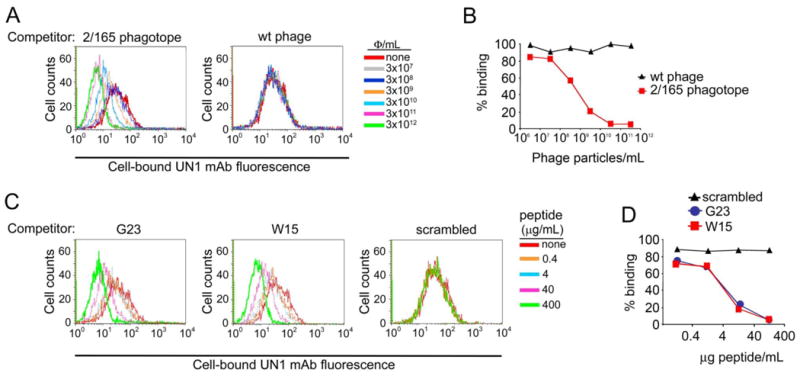
(A) Phagotope 2/165 inhibited the UN1 mAb binding to UN1-positive HPB-ALL cells. The mAb UN1 (0.37 μg/ml) was pre-incubated with the indicated doses of 2/165 phage (left panel) or wild type phage (right panel), and then added to HPB-ALL cells (5x105). Cell-bound UN1 mAb was revealed by flow cytometry. Histogram overlays of the UN1 mAb fluorescence intensity are shown. (B) Percentage of HPB-ALL cells recognized by mAb UN1 for the experiment described in A. (C) Synthetic peptides G23 and W15 inhibited the UN1 mAb binding to UN1-positive HPB-ALL cells. The mAb UN1 (0.37 μg/ml) was pre-incubated with the indicated doses of G23 (left panel), W15 (middle panel) or scrambled (right panel) peptides, and then added to HPB-ALL cells (5x105). Cell-bound UN1 mAb was revealed by flow cytometry. Histogram overlays of the UN1 mAb fluorescence intensity are shown. (D) Percentage of HPB-ALL cells recognized by mAb UN1 for the experiment described in B.
