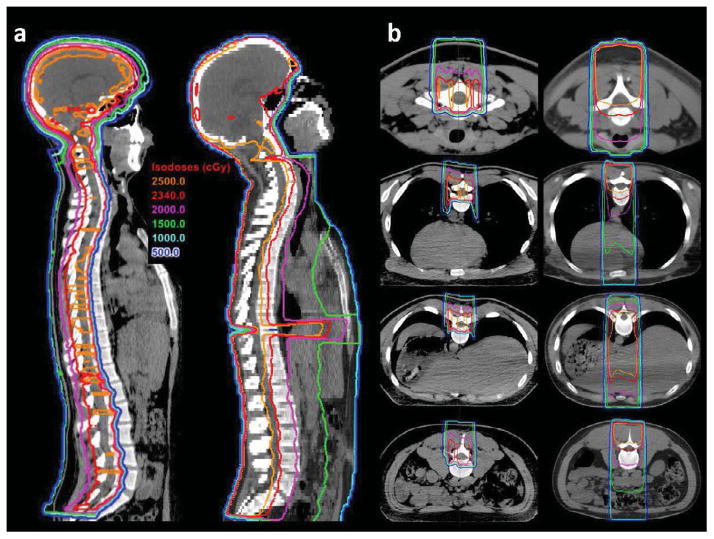
Figure 1.
Treatment planning computed tomography (CT) images in sagittal (panel a) and axial planes (panel b) comparing treatment plans for a proton craniospinal irradiation (CSI; left) and conventional photon CSI (right). The CSI prescription dose for each patient was 23.4 Gy. Isodose lines indicate significant reductions in doses delivered to the thyroid gland, esophagus, heart, lungs, liver, stomach, and bowel with proton CSI with sparing of the anterior vertebral bodies.