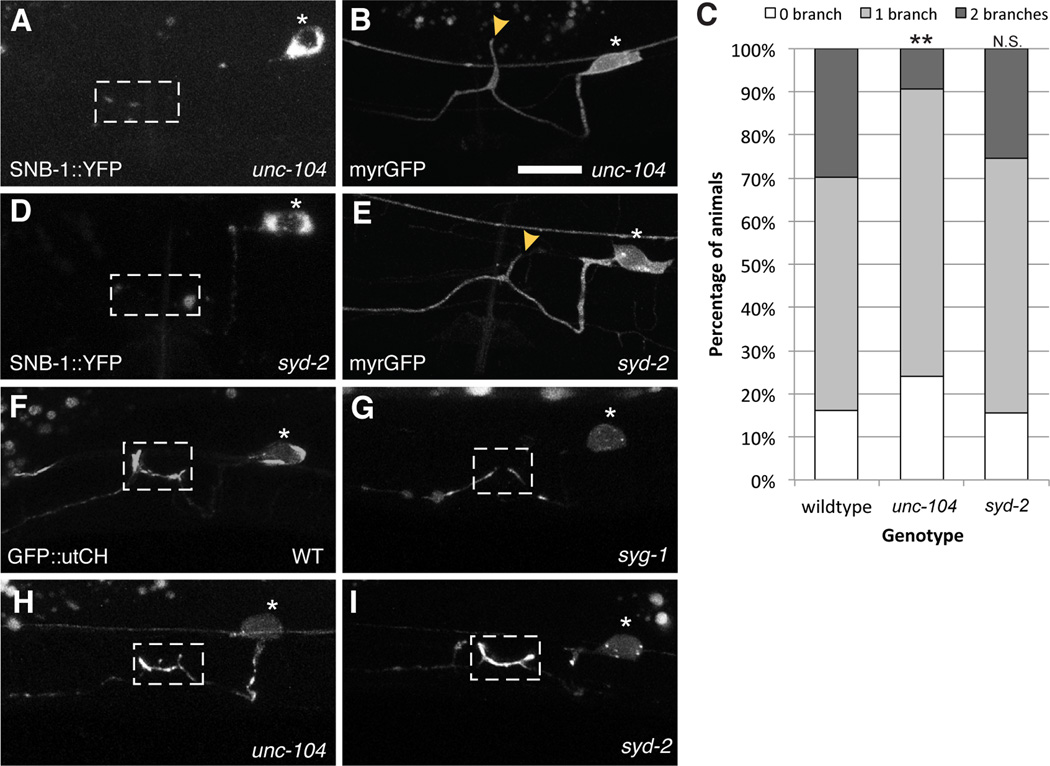
Figure 2. Synaptic vesicles and active zone proteins are not required for collateral branch formation.
(A) In kinesin motor unc-104 mutants, synaptic vesicles labeled by synaptobrevin::YFP fail to get transported to the synaptic region. (B) Loss of unc-104 results in a partial reduction in branch formation. (C) Graph quantifies the percentage of animals in each genotype that elaborate zero, one or two branches. Statistics for each mutant was from comparison with the wildtype values (**p<0.01 with n>100, Fisher’s exact test). (D) syd-2 mutants fail to accumulate synaptic vesicles and active zone molecules (E) but branches are unaffected in syd-2 mutants. (F) GFP::utrophinCH labels synaptic F-actin that is enriched at presynaptic specializations in the L4 stage. (G) This F-actin localization is loss in syg-1 mutants (H, I) but is unaffected in unc-104 and syd-2 mutants. Yellow arrowheads point to collateral branches. Scale bars represent 10 µm. See also Figure S1.