Abstract
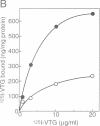
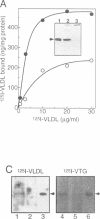
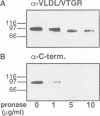
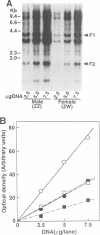
Deposition of the yolk mass components of chicken oocytes, very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and vitellogenin (VTG), is mediated by a 95 kDa plasma membrane protein, termed VLDL/VTG receptor (VLDL/VTGR). Molecular characterization of the VLDL/VTGR revealed that it is a member of the LDLR gene superfamily, and harbours eight complement-type, cysteine-rich ligand binding repeats at the N-terminus. This ligand binding domain structure is the hallmark of the recently discovered mammalian so-called VLDLRs, whose true physiological function remains to be elucidated. Northern blot analysis revealed that this receptor is expressed almost exclusively in oocytes, with very much lower levels of hybridizing transcripts present in heart and skeletal muscle. Heterologous expression of the cloned receptor demonstrated its ability to bind both VLDL and VTG. The receptor gene is located on the avian sex chromosome Z, in agreement with the sex linkage of a single-gene defect in animals that fail to reproduce because of the lack of expression of functional VLDL/VTGR. In situ hybridization analysis of oocytes suggested that VLDL/VTGR mRNA may relocalize during oocyte growth. Thus, the current study has identified and characterized the first non-mammalian VLDLR. Its key role in avian reproduction and extremely high evolutionary conservation shed new light on VLDLR function in mammals, which also express the gene in ovaries.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber D. L., Sanders E. J., Aebersold R., Schneider W. J. The receptor for yolk lipoprotein deposition in the chicken oocyte. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18761–18770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Schneider W. J., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Monoclonal antibodies to the low density lipoprotein receptor as probes for study of receptor-mediated endocytosis and the genetics of familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11923–11931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu G., Williams S., Strickland D. K., Schwartz A. L. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor is an hepatic receptor for tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7427–7431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. NPXY, a sequence often found in cytoplasmic tails, is required for coated pit-mediated internalization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3116–3123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
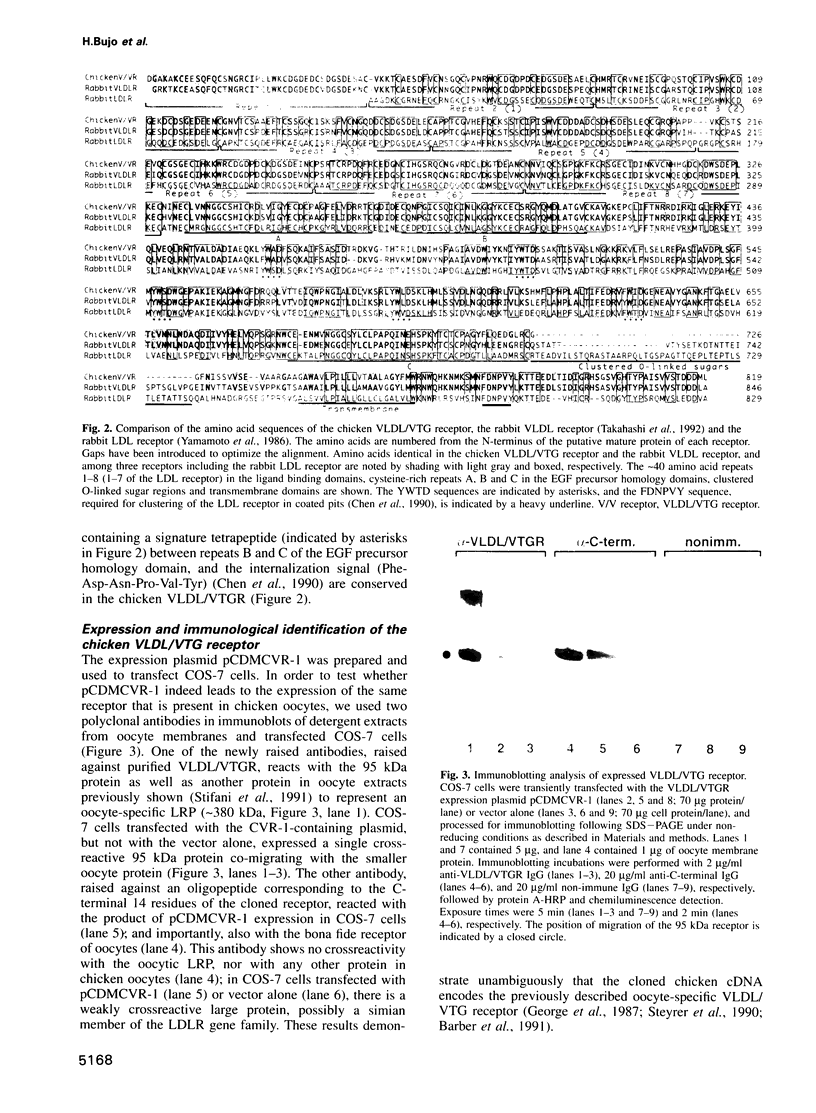
- George R., Barber D. L., Schneider W. J. Characterization of the chicken oocyte receptor for low and very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gåfvels M. E., Caird M., Britt D., Jackson C. L., Patterson D., Strauss J. F., 3rd Cloning of a cDNA encoding a putative human very low density lipoprotein/apolipoprotein E receptor and assignment of the gene to chromosome 9pter-p23. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;19(6):557–569. doi: 10.1007/BF01233382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Nimpf J., Schneider W. J. Chicken oocytes and fibroblasts express different apolipoproteins-B-specific receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3131–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Hamann U., Rogne S., Myklebost O., Gausepohl H., Stanley K. K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4119–4127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K. J., Lawrence W. D., Lewis L. A., Liu L. B., Taylor C. B. Hereditary hyperlipidemia in nonlaying chickens. Arch Pathol. 1974 Sep;98(3):161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer M. J., van Eck M. M., Petrij F., van der Zee A., de Wit E., Meijer D., Grosveld G., Havekes L. M., Hofker M. H., Frants R. R. The mouse low density lipoprotein receptor gene: cDNA sequence and exon-intron structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):880–886. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounnas M. Z., Morris R. E., Thompson M. R., FitzGerald D. J., Strickland D. K., Saelinger C. B. The alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein binds and internalizes Pseudomonas exotoxin A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12420–12423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumabe T., Sohma Y., Yamamoto T. Human cDNAs encoding elongation factor 1 gamma and the ribosomal protein L19. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2598–2598. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta K. D., Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low density lipoprotein receptor in Xenopus laevis. I. Five domains that resemble the human receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10406–10414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi P. K., Irace G., Van Jaarsveld P. P., Lippoldt R. E., Edelhoch H. Instability of coated vesicles in concentrated sucrose solutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5881–5885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., George R., Schneider W. J. Apolipoprotein specificity of the chicken oocyte receptor for low and very low density lipoproteins: lack of recognition of apolipoprotein VLDL-II. J Lipid Res. 1988 May;29(5):657–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., Radosavljevic M. J., Schneider W. J. Oocytes from the mutant restricted ovulator hen lack receptor for very low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1393–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., Stifani S., Bilous P. T., Schneider W. J. The somatic cell-specific low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein of the chicken. Close kinship to mammalian low density lipoprotein receptor gene family members. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Petersen C. M., Møller B., Jensen P. H., Moestrup S. K., Holtet T. L., Etzerodt M., Thøgersen H. C., Munch M., Andreasen P. A. Purified alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/LDL receptor-related protein binds urokinase.plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complex. Evidence that the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor mediates cellular degradation of urokinase receptor-bound complexes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14543–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka K., Tzung K. W., Sullivan M., Lindsay E., Baldini A., Chan L. Human very-low-density lipoprotein receptor complementary DNA and deduced amino acid sequence and localization of its gene (VLDLR) to chromosome band 9p24 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1994 Mar 15;20(2):298–300. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opresko L. K., Wiley H. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis in Xenopus oocytes. II. Evidence for two novel mechanisms of hormonal regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4116–4123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth K., Madison E. L., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. F., Herz J. Complexes of tissue-type plasminogen activator and its serpin inhibitor plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 are internalized by means of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7422–7426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. M., Gilbert A. B. Yolk transport in the ovarian follicle of the hen (Gallus domesticus): lipoprotein-like particles at the periphery of the oocyte in the rapid growth phase. J Cell Sci. 1979 Oct;39:257–272. doi: 10.1242/jcs.39.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychowdhury R., Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Smith J. A. Autoimmune target in Heymann nephritis is a glycoprotein with homology to the LDL receptor. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1163–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2786251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Different combinations of cysteine-rich repeats mediate binding of low density lipoprotein receptor to two different proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21682–21688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai J., Hoshino A., Takahashi S., Miura Y., Ishii H., Suzuki H., Kawarabayasi Y., Yamamoto T. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the human very low density lipoprotein receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2173–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Slaughter C. J., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Capra J. D., Brown M. S. Use of antipeptide antibodies to demonstrate external orientation of the NH2-terminus of the low density lipoprotein receptor in the plasma membrane of fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1635–1640. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J. The low density lipoprotein receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):303–317. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen X., Steyrer E., Retzek H., Sanders E. J., Schneider W. J. Chicken oocyte growth: receptor-mediated yolk deposition. Cell Tissue Res. 1993 Jun;272(3):459–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00318552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stifani S., Barber D. L., Aebersold R., Steyrer E., Shen X., Nimpf J., Schneider W. J. The laying hen expresses two different low density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19079–19087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stifani S., Barber D. L., Nimpf J., Schneider W. J. A single chicken oocyte plasma membrane protein mediates uptake of very low density lipoprotein and vitellogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1955–1959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Kawarabayasi Y., Nakai T., Sakai J., Yamamoto T. Rabbit very low density lipoprotein receptor: a low density lipoprotein receptor-like protein with distinct ligand specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9252–9256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall D. A., Patel S. The intracellular fate of vitellogenin in Xenopus oocytes is determined by its extracellular concentration during endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14779–14789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J. C., Patel D. D., Jones M. D., Knight B. L., Soutar A. K. Characterization and tissue-specific expression of the human 'very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor' mRNA. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):531–537. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willnow T. E., Orth K., Herz J. Molecular dissection of ligand binding sites on the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15827–15832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Bishop R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Deletion in cysteine-rich region of LDL receptor impedes transport to cell surface in WHHL rabbit. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1230–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3010466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yochem J., Greenwald I. A gene for a low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4572–4576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]