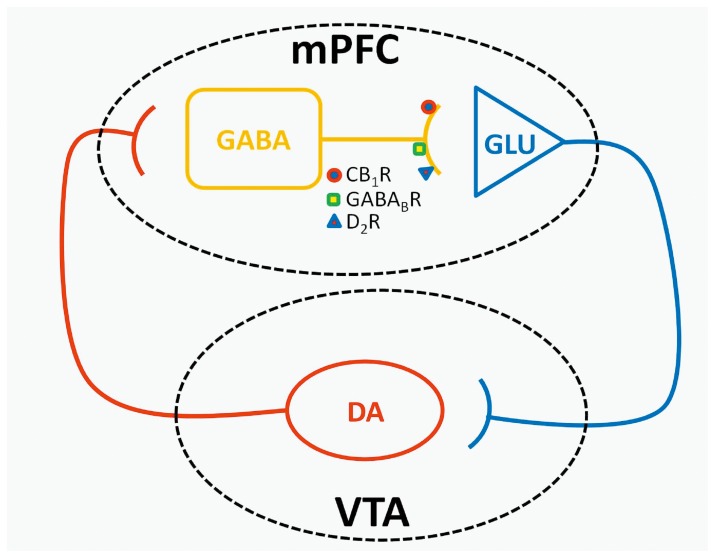
Figure 12. Representative scheme showing the main corticolimbic connections between the mPFC and VTA.
The main dopaminergic pathways that come from the VTA to the mPFC is highlighted. The excitatory action of dopamine on GABAergic interneurons in the mPFC leads to an increase of GABA release that, in turn, inhibits the activity of glutamatergic projecting neurons that, from the mPFC, innervate again the VTA. The decrease in the glutamate tone in VTA contributes to the reduction of dopaminergic neurons firing with the consequent release of dopamine in the mPFC. This negative feedback control regulates the dopamine output in mPFC.