Figure 1. NMO-IgG binds to AQP4 in rat astrocytes and produces CDC in the presence of rat complement.
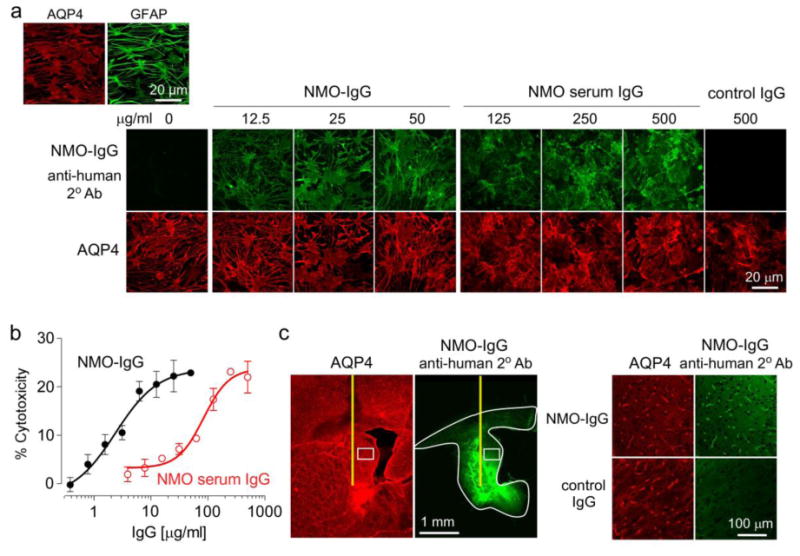
a. (Top left) AQP4 and GFAP immunofluorescence in well-differentiated primary cultures of rat astrocytes. (Bottom) Binding of NMO-IgG (recombinant human antibody rAb-53) or control IgG purified from NMO patient serum (each stained green with anti-human secondary antibody) to AQP4 (red). b. CDC (by Alamar blue assay) in rat astrocyte cultures following 3-h incubation with 5% rat complement and NMO-IgG or IgG purified from NMO patient serum (S.E., n=6). c. (Left) Immumofluorescence of brain sections at 3 h after intracerebral injection of 10 μg NMO-IgG showing area of antibody diffusion (white line). (Right) Expanded micrograph of boxed region along with data for control IgG.
