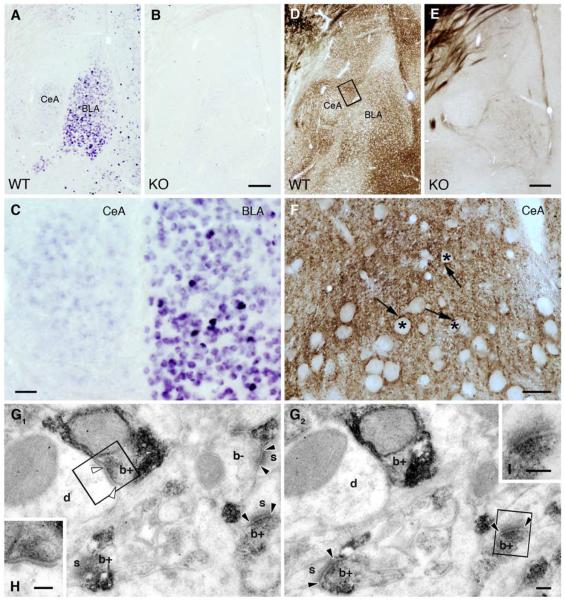
Figure 1. CB1 Receptors are Present on Excitatory Terminals in the CeAL.
(A) In situ hybridization reveals the presence of CB1 mRNA in both the CeA and the BLA of wild type mice. (B) The specificity of the riboprobe is confirmed by using CB1−/− animals. (C) The very high levels of CB1 mRNA observed in a few scattered neurons in the BLA likely correspond to GABAergic interneurons. The vast majority of BLA neurons express moderate levels of CB1 mRNA. In contrast, CB1 mRNA expression in the CeA was only slightly above detection threshold. (D–E) Immunoperoxidase staining demonstrates the presence of the CB1 protein in both the CeA and BLA, which was confirmed in our CB1−/− samples. (F) Higher magnification light micrographs reveal the dense CB1 labeling in the neuropil throughout the CeAL. Asterisks depict CB1-immunonegative cell bodies, whereas CB1-immunopositive labeling appears as punctate staining indicating the compartmentalized distribution of the protein. (G1-G2) Serial electron micrographs illustrate the selective presynaptic accumulation of CB1 in boutons (b+), which form mainly asymmetric (flanked by black arrowheads) and sometimes symmetric (white arrowheads) synapses with dendrites (d) and spine heads (s). CB1 staining remained under detection threshold in a few axon terminals (b−), which highlights quantitative differences in CB1 expression between terminal types innervating the CeAL. (H–I) The anatomical nature of the synapse type is illustrated at higher magnification. Scale bars: A, B, D, E are 200 μm; C is 50 μm; F is 20 μm; G1, G2, H, I are 100 nm.