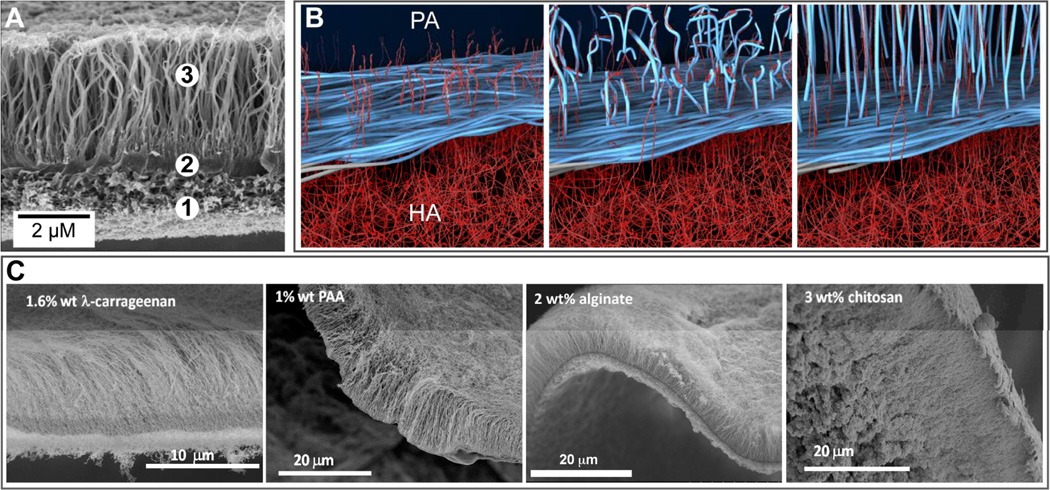
Fig. 9.
(A) Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a membrane formed at the liquid-liquid interface between an aqueous solution of the peptide amphiphile (PA) C16VVVAAAKKK and hyaluronic acid. The SEM shows the (1) amorphous region, (2) dense diffusion barrier, and (3) nanofibers aligned perpendicular to the interface. (B) Schematic representation illustrating the mechanism of diffusion barrier formation between the PA and HA aqueous compartments and the subsequent growth of aligned nanofibers over time. (C) From left to right, SEMs of hierarchical membranes formed with the PA in (A) and aqueous solutions of 1.6 wt% of the polysaccharide λ carrageenan, 1 wt% poly(acrylic acid) (PAA), 2 wt% alginate, or 3 wt% chitosan. (B) is adapted with permission from reference 9. Copyright 2008 AAAS.