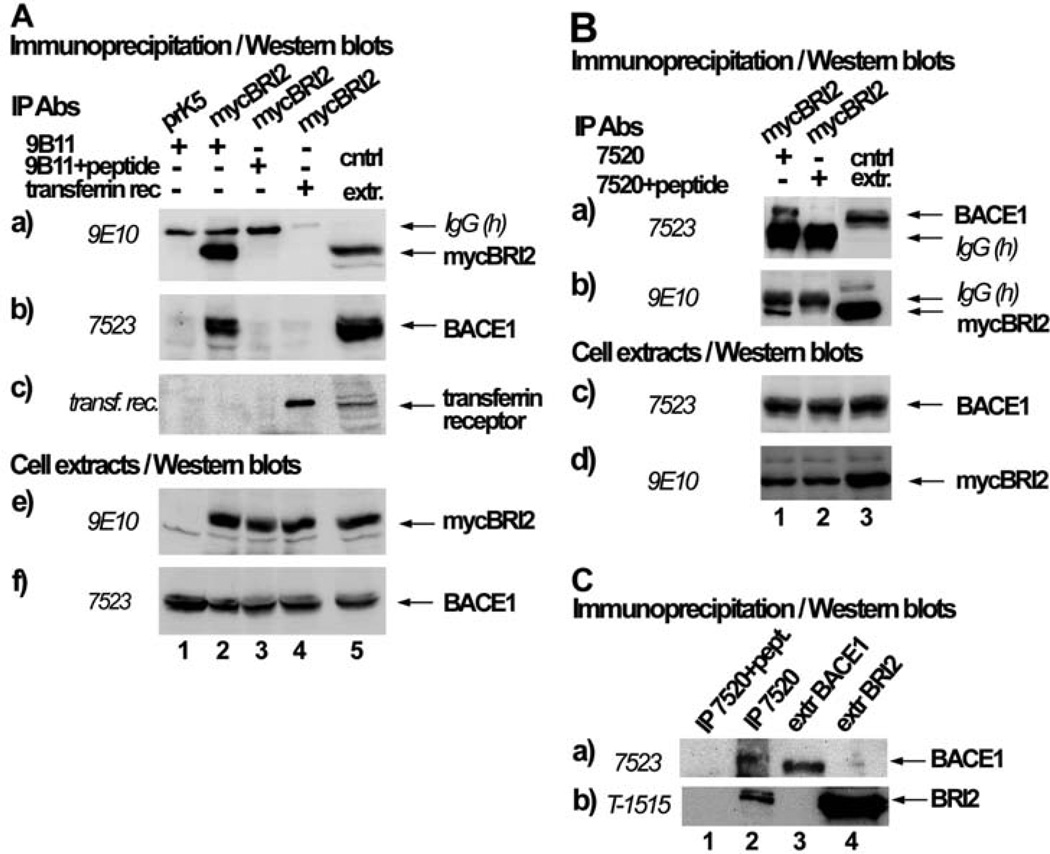
Fig. (2). BRI2 interacts specifically with BACE1.
(A) HEK293 cells were co-transfected with the cDNA encoding for BACE1 and either the myc-tag bearing vector, pRK5 (lane 1) or the cDNA encoding for myc-tagged BRI2 (mycBRI2) (lanes 2–4). Immunoprecipitates (IPs) with the anti-myc antibody 9B11 (to detect mycBRI2), 9B11 preabsorbed with its antigenic peptide or anti-transferrin receptor antibody were analyzed by western blot using the anti-myc antibody 9E10 (panel a), anti-BACE1 antibody 7523 (panel b), or the anti-transferrin receptor antibody (panel c). IgG(h) denotes the heavy chain of IgG. Extracts of cells expressing BACE1 or BACE1 and mycBRI2 were analyzed by western blot using the antibodies 9E10 (panel e) or 7523 (panel f). (B) HEK293 cells were co-transfected with cDNAs encoding for mycBRI2 and BACE1. IPs with the BACE1 specific antibody 7520 or 7520 preabsorbed with its antigenic peptide were analyzed by western blot using the anti-BACE1 antibody 7523 (panel a) or the anti-myc antibody 9E10 (panel b). Successful BACE1 and mycBRI2 expression can be seen in western blots in panels c and d, respectively. C. Extracts of SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with the BACE1 specific antibody 7520 or 7520 preabsorbed with its antigenic peptide and IPs and cell extracts were analyzed by western blot using the anti-BACE1 antibody 7523 (panel a) or the anti-BRI2 antibody T-1515 (panel b).