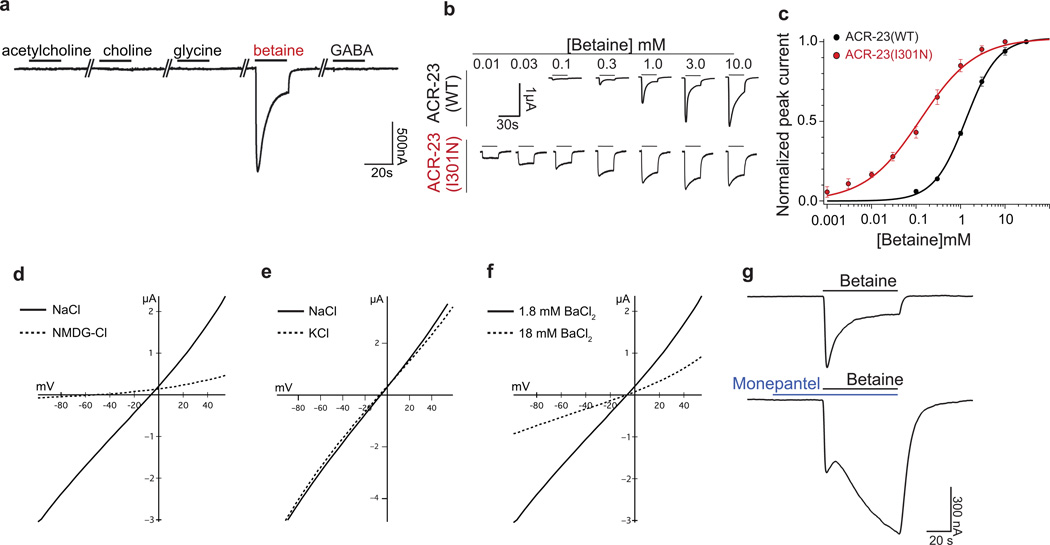
Figure 4. ACR-23 is a betaine-activated ion channel.
(a) Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing ACR-23 respond to a 20 s pulse of 1mM betaine, but not 1mM acetylcholine, choline, glycine, or GABA. The mean betaine-evoked response = 1.3 ± 0.13 µA for oocytes injected with 0.1 ng cRNA (n = 9 oocytes). (b) Representative betaine-evoked currents from oocytes expressing ACR-23 or ACR-23(I301N) stimulated with the indicated betaine concentration. (c) Betaine sensitivity of the wild-type ACR-23 channel (black line, n = 6 oocytes) and ACR-23(I301N) gain-of-function channel (red line, n = 5). EC50 is 1.4 mM for the wild type and 166 µM for ACR-23(I301N) (p = 0.0017). Error bars are means ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction. (d,e,f) ACR-23 is a monovalent cation channel. Insets indicate predicted ion flux under physiological conditions. (d) ACR-23 is permeable to sodium. Representative I-V curves in modified Ringer’s solution containing Na+ (n = 9) or NMDG (n = 8). (e) ACR-23 is potassium permeable. Representative I-V curves in modified Ringer’s solution containing Na+ (n = 7) or K+ (n = 7). (f) ACR-23 is not permeable to the divalent cation Ba2+. The reversal potential of betaine-evoked currents was not altered when extracellular Ba2+ concentration was increased 10-fold (n = 9). (g) Monepantel allosterically modulates ACR-23. A representative trace shows current induced by 1mM betaine in the absence (above) or presence (below) of 300 pM monepantel in oocytes expressing ACR-23 (n = 11).