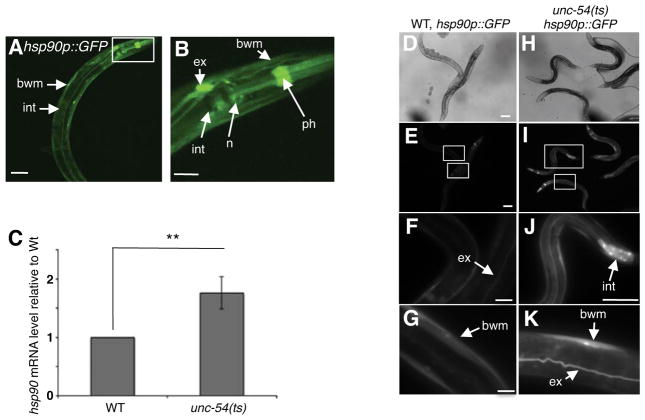
Figure 1. Tissue-specific perturbation of proteostasis is recognized across multiple tissues in a cell-non-autonomous manner.
(A,B) Confocal image of a young adult animal expressing the 2.5 kb hsp90 promoter region upstream of GFP (hsp90p::GFP) at 20°C. Pronounced expression was observed in mu ltiple tissues, including pharyngeal muscle (ph), intestine (int), pharyngeal nerve ring (n), bodywall muscle (bwm) and the excretory cell (ex). Scale bar is equal to 100 μm. (B) 63x magnification of the head region. Expression is detected in the bodywall muscle (bwm), the excretory cell (ex), the pharyngeal muscle (ph), pharyngeal nerve-ring (n) and the intestine (int). Scale bar is equal to 10 μm. (C) Total mRNA levels of hsp90 in unc-54(e1301) animals relative to wild type at 15C°C. Bargraphs represent combined mean values of three independent experiments (means ± s.e.m.) **P-value < 0.01. (D–K) hsp90p::GFP reporter expression in unc-54(e1301) animals compared to wild type. Scale bar of figures (D–K) are equal to 100 μm. (F,G) 100x image of wild type expressing the hsp90 reporter in the excretory canal (ex) and bodywall muscle (bwm). (J,K) hsp90 expression in intestinal cells, bodywall muscle and excretory canal in unc-54(e1301) animals. (J) 40x image. (K) 100x image. All fluorescent images were taken at equal exposure times. See also Figure S1.