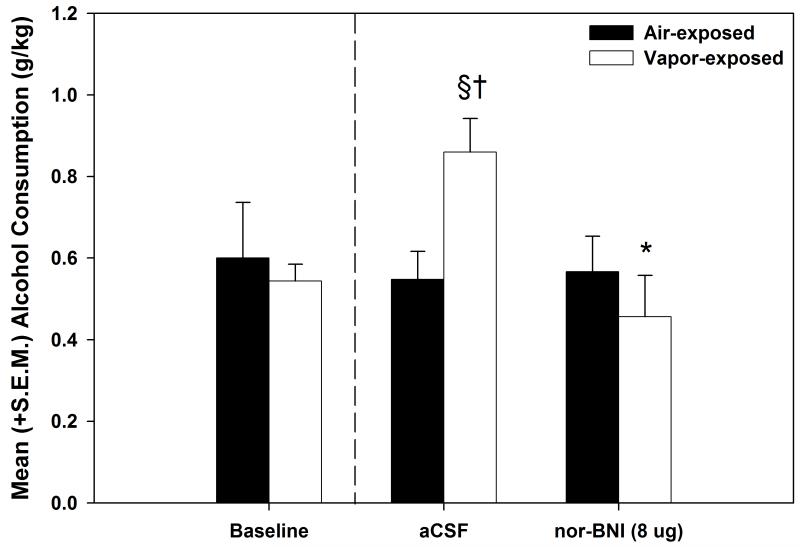
Figure 3. Effect of nor-BNI on nondependent and ethanol-dependent ethanol self-administration.
Mean (+S.E.M.) ethanol consumption (g/kg) during baseline, aCSF-treated and pharmacological challenge with nor-BNI for air-exposed (n=9) and alcohol vapor-exposed (n=8) rats. Following a one-month dependence induction period (represented by the dashed line), the animals received bilateral sham and aCSF infusions (0.5 μl/side over 2 min). After confirmation that responding was unaffected by the site-specific control infusions, norBNI (4 μg/side over 2 min) was infused prior to a final self-administration session. Nor-BNI selectively reduced operant self-administration for alcohol in the vapor-exposed dependent animals while leaving nondependent responding intact († = p < 0.05 when compared to the corresponding air-exposed group, § = p < 0.05 when compared to baseline of the same exposure condition, * = p < 0.05 when compared to the vapor-exposed aCSF-treated group).