Figure 1.
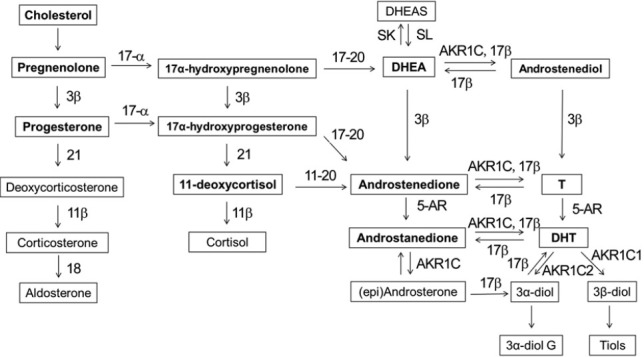
Pathway of steroid biosynthesis and the conversion of T to DHT by 5-AR. C21 precursors (pregnenolone and progesterone) are converted to C19 adrenal androgens (DHEA and androstenedione) by sequential hydroxylase and lyase activities. Circulating adrenal androgens enter the prostate and can be converted to T or androstanedione by a series of reactions involving the activity of 3β and 17β enzymes. T is then converted to the potent androgen DHT by the activity of 5-AR. 17α: 17α-hydroxylase; 17,20: 17,20-lyase; 21: 21-hydroxylase; 3β: 3-HSD (hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase); 17β: 17-HSD (hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase); DHEA: dihydroepiandrosterone; AKR1C: aldo-keto reductase; 3α-diol: 5α-androstane-3α, 17β-diol; 3β-diol: 5α-androstane-3β, 17β-diol.
