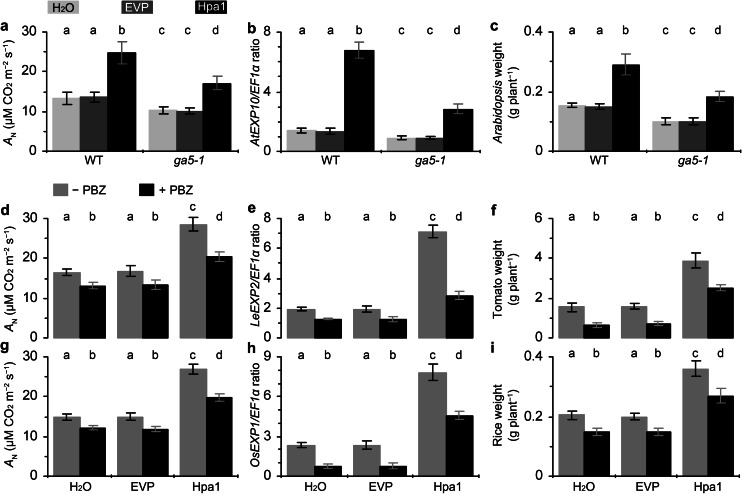
Fig. 8.
The inhibitory effects of genetic or chemical blocking in gibberellin biosynthesis on Hpa1-induced enhancements of photosynthesis, EXP expression, and plant growth. a–c The Arabidopsis mutant ga5-1, which has a defect in gibberellin biosynthesis, was tested together with the WT plant in the experiments. Ten-day-old plants were treated separately with an aqueous Hpa1 solution and with water or an aqueous EVP solution. d–i The gibberellin biosynthesis inhibitor PBZ was used to inhibit gibberellin biosynthesis in tomato (d–f) and rice (g–i) plants. Ten-day-old plants were treated separately with Hpa1 and Silwet-37 in the presence of PBZ (+ PBZ) and the absence of PBZ (–PBZ). a–i Five days after plant treatment, analyses of A N rates and EXP expression were performed on the second youngest leaves. Fresh weight of plants was scored 10 days after treatment. Data are shown as mean values ± SD from three experimental repeats (15 plants per repeat). Different letters on tops of bar graphs indicate significant differences by two-tailed ANOVA and LSD test (P < 0.01)