Figure 1. Generation of HNSCC xenograft model of acquired resistance to bevacizumab.
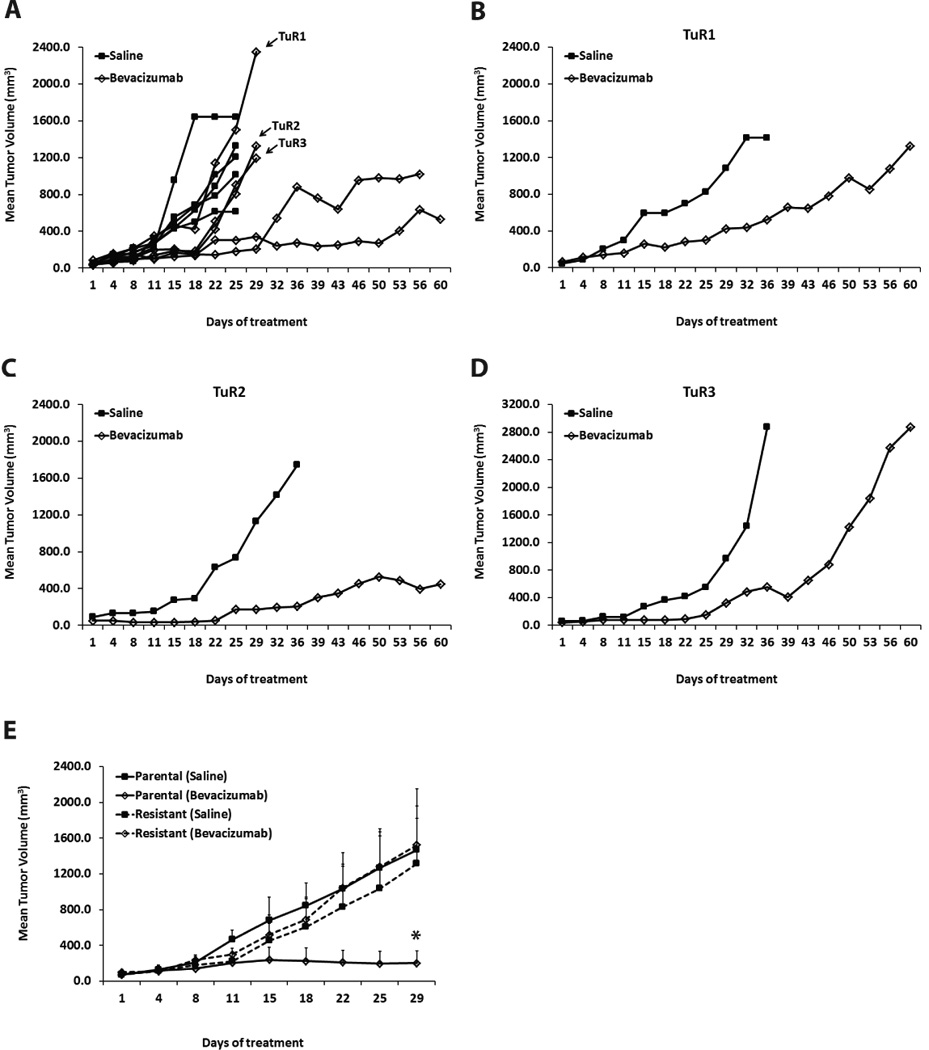
(A) Growth curve of Tu138 xenografts (n=5 per group) treated with saline or bevacizumab at an initial dose of 4mg/kg followed by incrementing the dose by 4mg/kg with every subsequent increase in tumor volume. 3/5 xenograft tumors (TuR1, TuR2 and TuR3) showed resistance with growth rates comparable to the saline control. (B–D) Resistant xenografts were excised and small tumor fragments were reimplanted into new mice (n=2) to propagate the model. Reimplanted tumors were subjected to a second phase of treatment with saline or bevacizumab (increasing concentrations, 8mg/kg–20mg/kg). Emergence of resistance was observed in bevacizumab-treated tumor TuR1 and TuR3 while TuR2 remained fairly sensitive. (E) Validation of acquired resistance in reimplanted TuR3 resistant tumors by treating xenografts (n=4 per group) with saline or bevacizumab. Parental Tu138 tumors were sensitive to bevacizumab resulting in 88% growth inhibition (* P=0.0171). In contrast, the resistant tumors showed no significant reduction in tumor growth.
