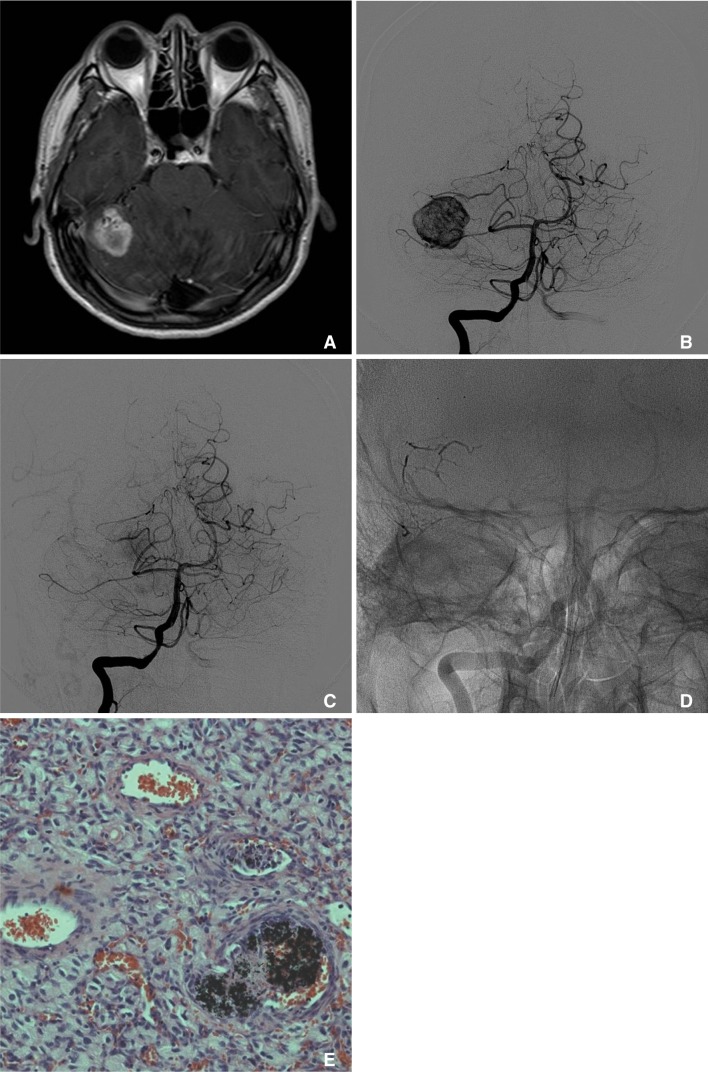
Fig. 1.
A. Brain MRI (Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image) reveals a 2.7 × 2.5 cm sized heterogeneously enhancing tumor with multiple signal void vascular structure within the tumor in the right cerebellar hemisphere. B. Diagnostic angiogram reveals the high vascularity with AV shunting within the tumor, which is characteristic for hemangioblastoma. C. The patient undergoes embolization of two distal pedicles off the right superior cerebellar artery using Onyx, resulting in near complete resolution of the tumor blush. D. Native cranial view in posteroanterior projection demonstrates a dense Onyx cast within mural nodule of the tumor. E. Histological examination of the excised tumor shows that the hemangioblastoma is composed of stromal cells, which show characteristically large and vacuolated appearance, and abundant vascular cells, such as endothelial cells and pericytes. Nidus vessels are occluded with thrombus and black colored embolic material, Onyx.