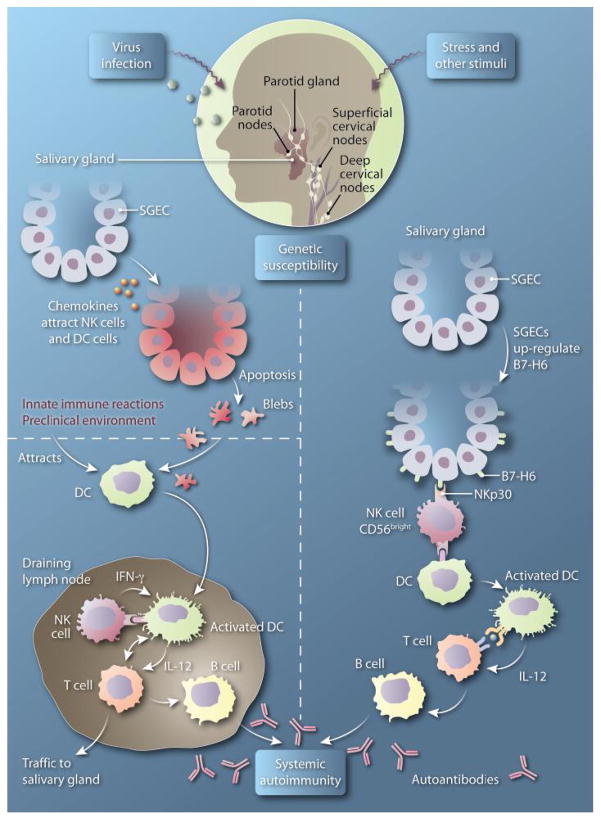
Fig. 1. Other little helper.
(Left) In lymph nodes that drain the salivary glands, NK cells interact with DCs carrying apoptotic debris from SGECs, resulting in DC maturation. Mature DCs interact with and activate T cells, which then couple with and activate B cells, thus initiating the systemic autoimmune response. (Right) Within the salivary glands, NKp30-expressing NK cells interact with SGECs that express B7-H6. This interaction leads to the production of multiple chemokines, which spurs inflammatory cell infiltration within the salivary gland. NK-activated DCs interact with infiltrating T cells. The resulting activated T cells couple with and activate B cells, which produce autoantibodies and thus initiate and sustain a localized autoimmune response. IL-12, interleukin-12.