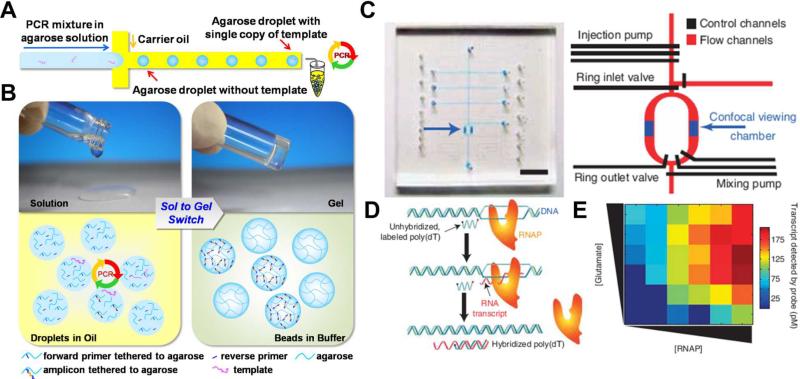
Fig. 1.
(A) Agarose emulsion droplet microfluidic method for single-molecule emulsion polymerase chain reactions (PCR). Microfluidic channels are used to isolate single copies of template DNA through droplet formation. Droplets are generated such that each contains either single copy of DNA template, or none. PCR products are later collected from each droplet separately from the outlet. (B) Sol to gel switch allows ePCR in aqueous droplet and confinement of PCR product in gelated agarose beads. (C) Optical image and schematic design of the optofluidic-based high-throughput smFRET analyses. Various pumps and valves are used to control the injection and mixing of reagents with different concentrations for sequential and automatic single-molecule. The scale bar is 5 mm. (D) Scheme of RNA polymerase transcript assay. (E) Heat map of transcription activities at various glutamate and RNA polymerase concentrations obtained directly through programmable control of the optofluidic-based analysis platform. Images are reproduced from Ref. 20 and 21.