Fig. 3.
Ca2+ handling properties and Ca2+-related alternans
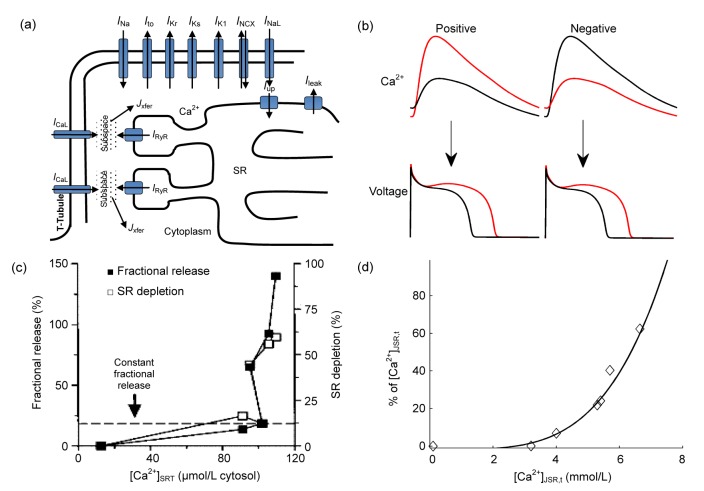
(a) Schematic of the ventricular intracellular Ca2+ handling components and the main ionic currents involved in depolarization and repolarization (I Na: fast Na+ current; I to: transient outward K+ current; I Kr: rapid delayed rectifier K+ current; I Ks: slow delayed rectifier K+ current; I K1: time-independent K+ current; I NCX: Na+-Ca2+ exchange current; I NaL: late Na+ current; I CaL: L-type Ca2+ channel (LCC) current; I up: pump current; I leak: leak current; I RyR: ryanodine receptor current; J xfer: Ca2+ flux transferred from subspace to the cytosol). (b) Illustration of positive and negative Ca2+→voltage couplings. Positive (negative) coupling refers to the case that a larger Ca2+ transient is accompanied with a longer (shorter) APD during the same beat at a constant CL. (c) Experimentally measured fractional SR Ca2+ release as a function of [Ca2+]SRT (total Ca2+ content in SR), reproduced with permission from Shannon et al. (2000). (d) Simulated fractional SR Ca2+ release from our work (Zang et al., 2013). [Ca2+]JSR,t: total Ca2+ content in junctional SR (JSR)