Table 3.
Representative examples of the mixed behavioral patterns revealed by studies examining how stimulus content or features of the arousal response influence the effect of arousal on memory.
| Manipulation Category | Specific Manipulation | Study | Key Finding for Effect of Arousal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content of Memoranda | Emotional vs. neutral | Abercrombie et al., 2003 |
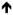 Negative and Neutral Negative and Neutral |
| Buchanan & Lovallo, 2001 |
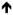 Positive and Negative; No effect on Neutral Positive and Negative; No effect on Neutral |
||
| Cahill, Gorski, & Le, 2003 |
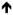 Negative; No effect on Neutral Negative; No effect on Neutral |
||
| Payne et al., 2007 |
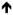 Negative; Negative;
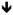 Neutral Neutral |
||
| Rimmele et al., 2003 |
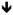 Negative; Negative;
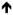 Neutral Neutral |
||
| Schwabe & Wolf, 2010 |
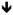 Positive, Negative, Neutral Positive, Negative, Neutral |
||
| Positive vs. negative valence | Domes et al., 2004 |
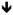 Positive; No effect on Negative Positive; No effect on Negative |
|
| Schwabe et al., 2008 |
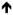 Negative; No effect on Positive Negative; No effect on Positive |
||
| Memoranda related, or unrelated, to stressor | Smeets et al., 2007 | Memory for stressor-related words > Non-stressor-related words | |
| Smeets et al., 2009 | Memory for stressor-related words > Non-stressor-related words | ||
| Memoranda central or peripheral to the elicitor of arousal | Christianson, 1984 |
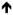 Central; No effect on Peripheral Central; No effect on Peripheral |
|
| Easterbrook, 1959 | Cue-utilization:
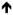 Central; Central;
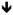 Peripheral Peripheral |
||
| Heuer & Reisberg, 1990 |
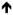 Central and Peripheral Central and Peripheral |
||
| Kebeck & Lohaus, 1986 |
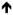 Central; Central;
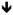 Peripheral Peripheral |
||
| Loftus, Loftus, & Messo, 1987 | Weapon focus effect:
 Central; Central;
 Peripheral Peripheral |
||
| Salience of neutral stimuli | Sutherland & Mather, 2012 |
 High-salience stimuli; No effect on Low-salience stimuli High-salience stimuli; No effect on Low-salience stimuli |
|
|
| |||
| Features of Arousal | Level of Arousal | Gold & Van Buskirk, 1975 | Inverted-U; moderate (not lower or higher) doses of epinephrine enhance spatial memory |
| Lupien et al., 1997 | High stress
 memory for unrelated pairs of words memory for unrelated pairs of words |
||
| Yerkes & Dodson, 1908 | Inverted-U between shock strength and learning success on complex tasks | ||
| Relevance of Arousal to Task: Reason for physiological arousal | Libkuman et al., 1999 | Task-relevant arousal
 memory for scene details Task-Irrelevant = No effect memory for scene details Task-Irrelevant = No effect |
|
