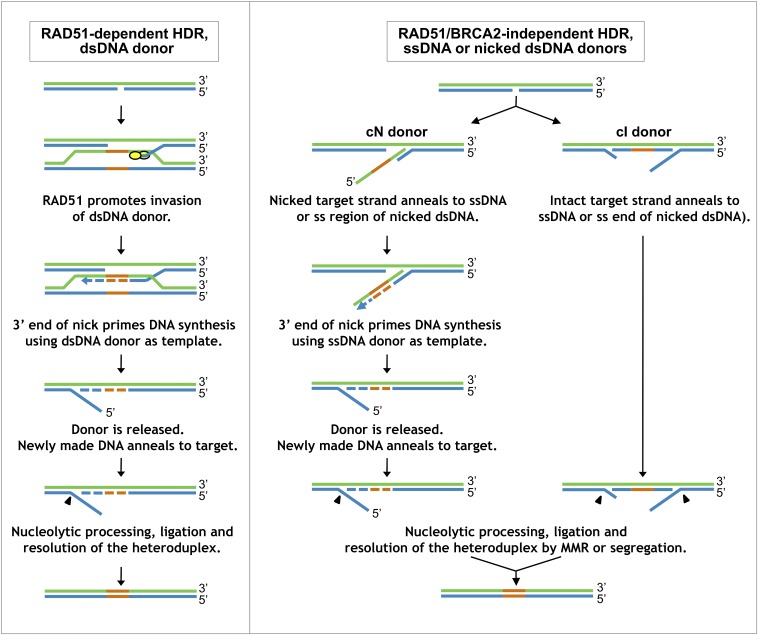
Fig. 6.
Working model for pathways of HDR at nicks. (Left) RAD51-dependent HDR using a dsDNA donor. A gap is exposed at the nicked target, and BRCA2 loads RAD51 on the free 3′ end, enabling invasion of a homologous dsDNA donor, as in canonical DSB repair. (Right) RAD51/BRCA2-independent HDR. A gap is exposed at the nicked target, and the donor anneals to either the nicked (Left) or intact (Right) strand of the duplex, independent of RAD51/BRCA2. Heterology (orange) and repair synthesis (dashed line) are shown. Arrowheads represent nucleolytic removal of DNA, either by excision or flap cleavage. Refer to Discussion for more detailed description; Fig. S5 for more complete diagrams of mismatch repair and ligation steps; and Figs. S6 and S7 for diagrams of how nicked dsDNA donors may participate in this pathway. MMR, mismatch repair.