Fig. 2.
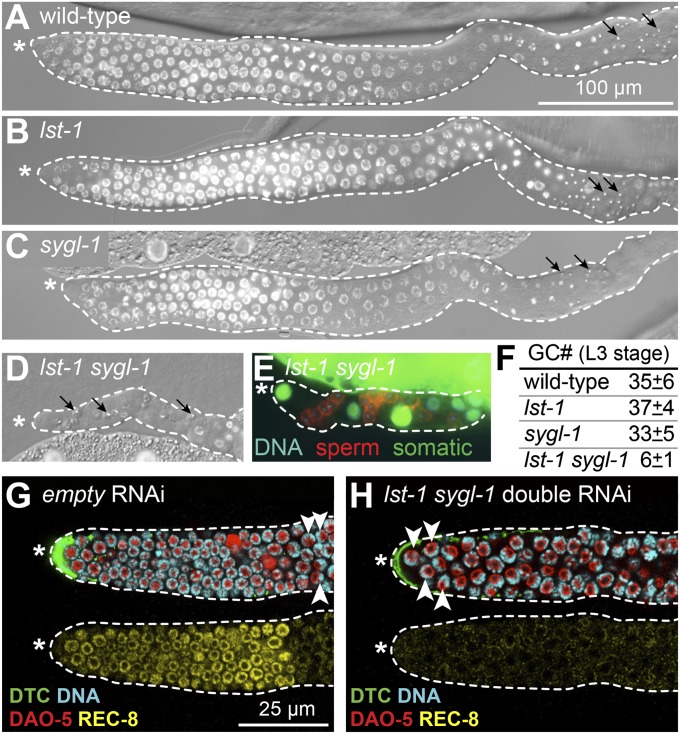
lst-1 and sygl-1 function redundantly to promote GSC self-renewal in larvae and adults. (A–D) DIC- and DAPI-stained images of gonads dissected from L4 hermaphrodites. Asterisk marks distal end; dotted line outlines germ line plus somatic gonadal cells; arrows mark mature sperm. (A–C) Wild type (100% non-Glp; n > 100), lst-1(ok814) (100% non-Glp; n = 146), and sygl-1(tm5040) (100% non-Glp; n = 159) all produce normal germ lines. (D) lst-1 sygl-1 double mutants produce Glp germ lines with only a few differentiated sperm (100% Glp; n = 76). (E) Gonad from lst-1 sygl-1 L4 with a somatic GFP marker (green), a sperm marker (red) and DNA staining (blue). All nonsperm cells expressed somatic GFP. Each gonadal arm contained 14 ± 3 sperm (n = 9) on average (from three to four premeiotic germ cells). (F) Total premeiotic germ cells (GC#) in entire L3 gonad, scored with PGL-1 germ cell marker. For wild-type and each single mutant, n = 5; for lst-1 sygl-1 double mutant, n = 9. (G–H) Representative confocal images of wild-type late L4 larval germ lines treated with RNAi for 48 h; DTC expresses GFP (green). Same conventions as in A–D; mitotic zone scored by presence of mitotic marker REC-8 (yellow) and absence of crescent-shaped DAPI staining typical of early meiotic prophase nuclei (white arrowheads). Anti–DAO-5 (red, nucleolar marker) counter stain facilitates scoring of DAPI crescents. (G) Germ line treated with empty RNAi vector possesses a mitotic zone. (H) Germ line treated with lst-1 sygl-1 double RNAi lacks a mitotic zone and hence lacks GSCs.