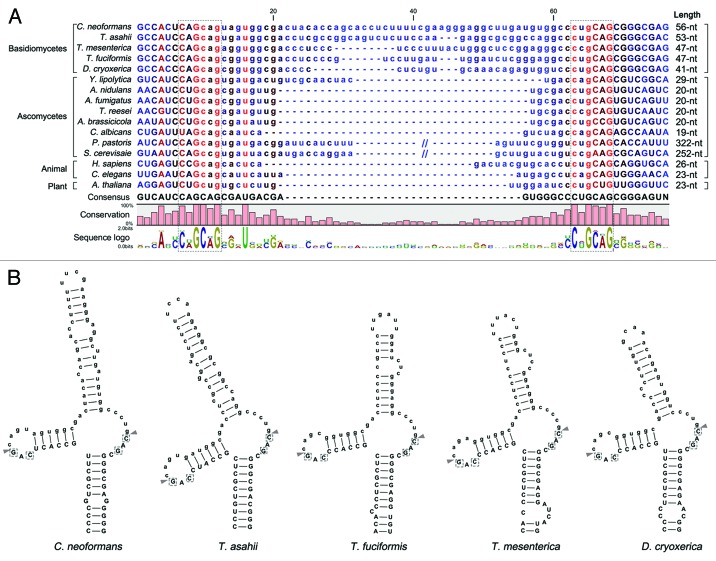
Figure 2. Conservation of the putative unconventional splicing sites of HXL1 homologs in basidiomycetes. (A) The unconventional intron sequences of HAC1/XBP1/HXL1 homologous mRNAs are aligned. Flanking exon sequences are denoted by uppercase letters and intron sequences by lowercase letters. Length indicates nucleotide length of the non-conventional intron that can be removed by Ire1. The conserved sequences of 5′- and 3′- splicing junctions are represented by sequence logo and dotted box. (B) Predicted secondary mRNA structures of HXL1 homologs in some basidiomycetous fungi. Putative splicing sites in 5′ and 3′ intron borders are located in the loop regions of stem-loop structures. The putative Ire1-mediated splicing sites and introns are indicated with arrowheads and written in lower case, respectively. Conserved sequences in splicing junctions are indicated by dotted boxes. Alignment and RNA secondary structure prediction were performed with the CLC main benchwork 6.8.4 (CLC bio). Nucleotide sequences were retrieved from the NCBI database and fungal genomics resource at JGI61: Cryptococcus neoformans (HXL1, CNAG_06134), Trichosporon asahii (A1Q2_03745), Tremella mesenterica (TREMEDRAFT_57223), Tremella fuciformis (bZIP1, GU723640.1), Dioszegia cryoxerica (fgenesh1_kg.80_#_88_#_Locus1962v1rpkm301.65), Yarrowia lipolytica (HAC1, XM_500811.1), Aspergillus nidulans (hacA, AJ413273), Aspergillus fumigatus (hacA, XM_743634), Trichoderma reesei (hac1, AJ413272), Alternaria brassicicola (HacA, AB01954.1), Candida albicans (HAC1, EF655649), Pichia pastoris (HAC1, FN392319), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (HAC1, NC_001138.5), Homo sapiens (XBP1, NM_005080), Caenorhabditis elegans (xbp-1, AF443190), Arabidopsis thaliana (bZIP60, AY045964).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.