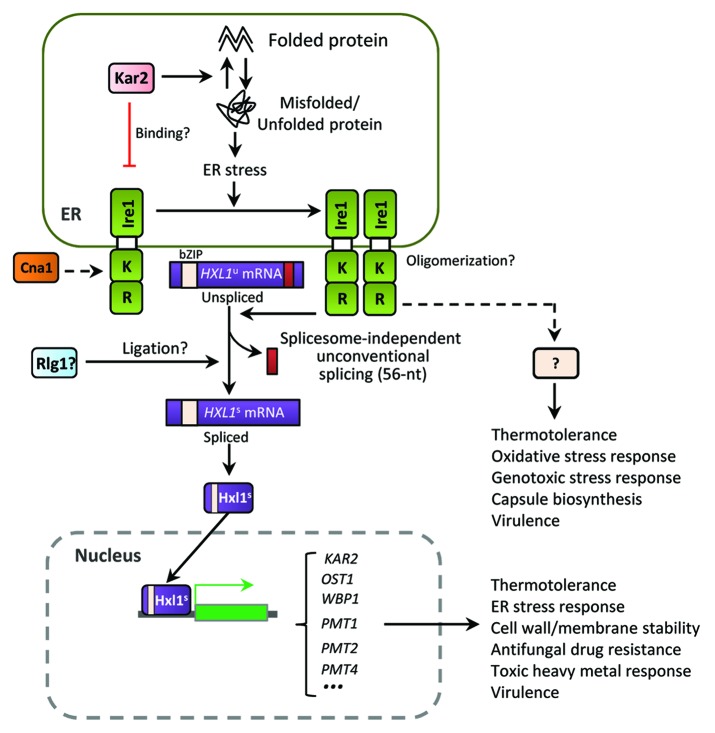
Figure 3. The ER stress response and UPR pathways in C. neoformans. The Cryptococcus UPR pathway consists of the Ire1 kinase, a bZIP transcription factor Hxl1, and their target genes. Upon ER stress, the spliceosome-independent unconventional splicing event in HXL1 mRNA occurs. Activated Hxl1 translocates to the nucleus and induces the expression of UPR target genes such as KAR2, which encodes an ER-resident molecular chaperone. The UPR pathway plays Ire1/Hxl1-dependent roles in ER stress response, antifungal drug resistance, and virulence. However, Ire1 also appears to have Hxl1-independent functions. Crosstalk between the UPR and calcineurin pathways via Cna1 is also indicated in Cryptococcus. Black arrows represent positive regulation or activation whereas red barred lines indicate negative regulation or repression. Dotted arrows indicate potential or unclear regulation.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.