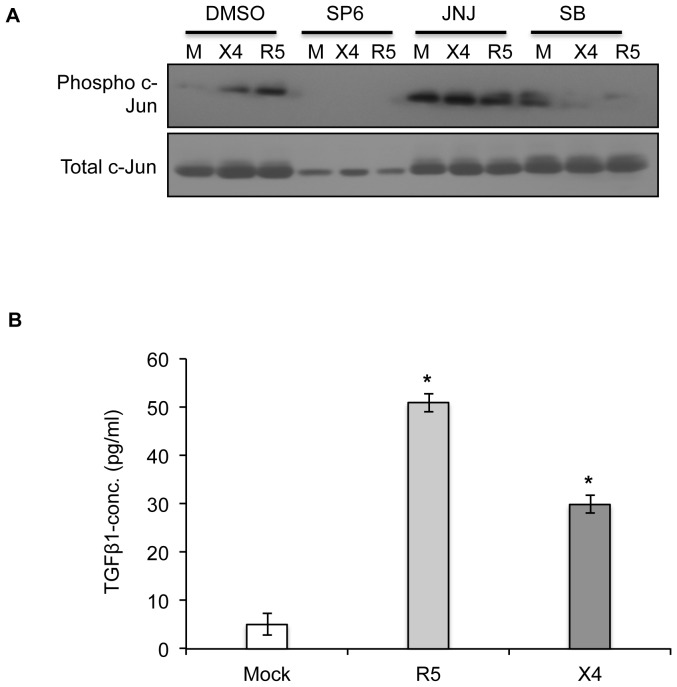
Figure 6. TGF-β is responsible for the indirect effects of HIV-1 infection on hepatic stellate cells.
(A) Serum-starved LX2 cells were treated with 25 µM SP600125 (JNK inhibitor), 15 nM JNJ10198409 (PDGF inhibitor) or 10 µM SB-431542 (TGF-β inhibitor) for 2 hr; DMSO was used as control. Culture supernatants from HIV infected PBMCs (mock (M), X4- or R5-) were then added on LX2 cells in the ratio of 1∶3 for 72 hr together with replenishment of inhibitor after every 24 hr. Cell lysates were prepared and phospho-c-Jun and total c-Jun (loading control) levels were determined by western blotting. (B) Culture supernatants from HIV infected PBMCs (mock, X4- or R5-) that were used for the treatment of LX2 cells were evaluated for the levels of TGF-β1 cytokine using ELISA. Data represents the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. *p<0.001 vs mock.