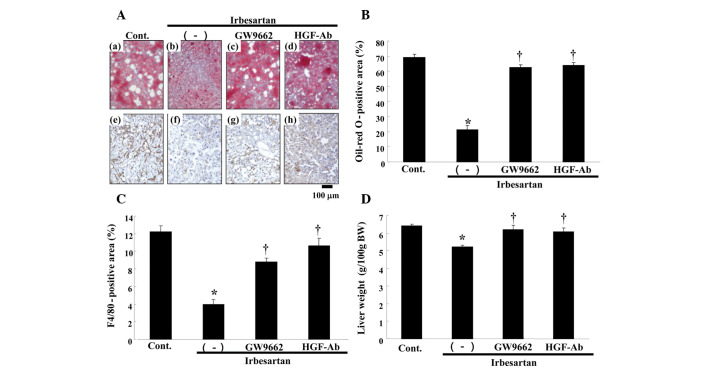
Figure 4.
Effects of irbesartan, GW9662 and hepatocyte growth factor neutralizing antibody (HGF-Ab) on liver. (A) Upper panels: typical micro-graphs of periodic cross-sections of liver with oil-red O staining after 12 weeks of high-fat diet (HFD). (a) Control (HFD only), (b) HFD + irbesartan (5 mg/kg/day), (c) HFD + irbesartan + GW9662, a PPARγ antagonist (0.5 mg/kg/day) and (d) HFD + irbesartan + neutralizing antibody against HGF (200 μg/week); bar, 100 μm. Lower panels: typical micrographs of immunostaining for macrophages (F4/80) in periodic cross-sections of liver tissue after 12 weeks of HFD. Brown-stained area shows F4/80 protein-positive area; (e) control (HFD only), (f) HFD + irbesartan (5 mg/kg/day), (g) HFD + irbesartan + GW9662, a PPARγ antagonist (0.5 mg/kg/day) and (h) HFD + irbesartan + neutralizing antibody against HGF (200 μg/week); bar, 100 μm. (B) Quantitative data for percentage of oil deposits (oil-red O-positive area) in liver. (C) Quantitative data of immunohistochemical staining for macrophages (F4/80) in liver (%). (D) Liver weight [g/100g of body weight (BW)]. Control, HFD only; (−), HFD + irbesartan (5 mg/kg/day); GW9662, HFD + irbesartan + GW9662, a PPARγ antagonist (0.5 mg/kg/day); HGF-Ab, HFD + irbesartan + neutralizing antibody against HGF (200 μg/week). *P<0.01 vs. control, †P<0.05 vs. irbesartan only. PPARγ; peroxisome proliferators activated receptor-γ.