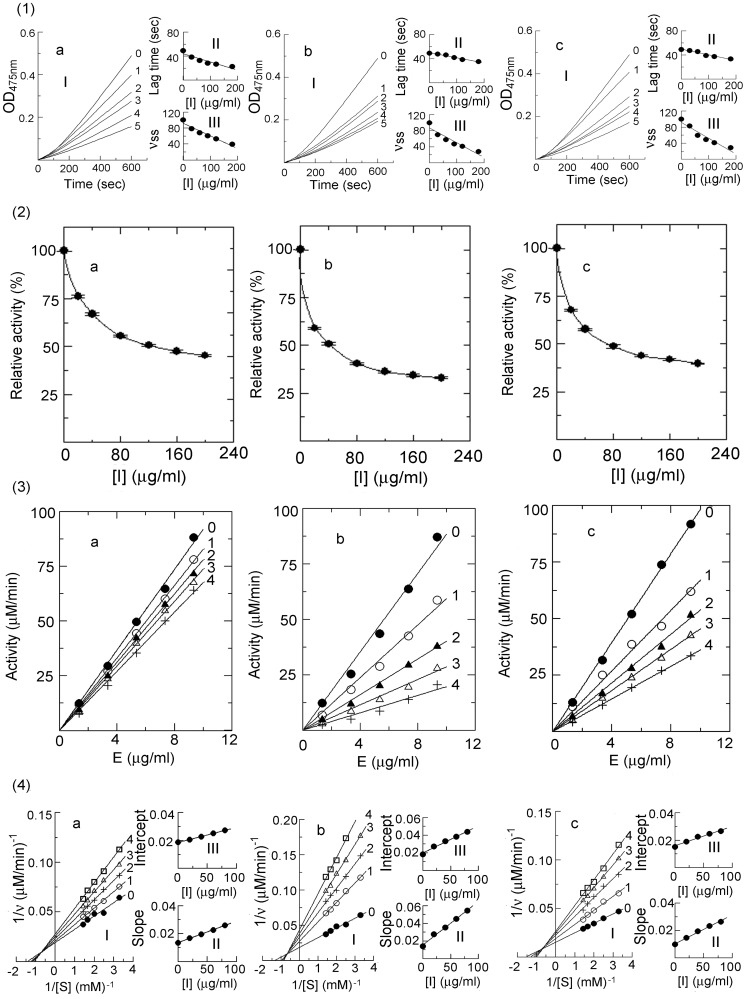
Figure 5. Determination of the inhibitory activity, inhibition mechanism, type, and constants.
(1) Inhibitory activity of the condensed tannins on monophenolase activity of mushroom tyrosinase. (I) Progress curves for the oxidation of L-Tyr by the enzyme. (II) Effects on the oxidation rate of L-Tyr by the enzyme. (III) Effects on the lag time of monophenolase. The concentrations of the condensed tannins for curves 0–5 were 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 μg/ml, respectively. (2) Inhibitory activity of the condensed tannins on diphenolase activity of mushroom tyrosinase. (3) Inhibition mechanism of the condensed tannins on mushroom tyrosinase. The concentrations of the condensed tannins for curves 0–4 were 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80 μg/ml, respectively. (4) Determination of the inhibition type and constants of the condensed tannins on mushroom tyrosinase. (I) Lineweaver-Burk plots for diphenolase activity. (II) The plot of slope versus the concentration of the condensed tannins for determining the inhibition constants KI. (III) The plot of intercept versus the concentration of the condensed tannins for determining the inhibition constants KIS. Assay conditions: 3 ml reaction system containing 50 mM phosphate sodium buffer (pH 6.8) and 3.3% DMSO. a, b, and c represented the condensed tannins from leaves, fruit, and stem bark of F. virens, respectively.