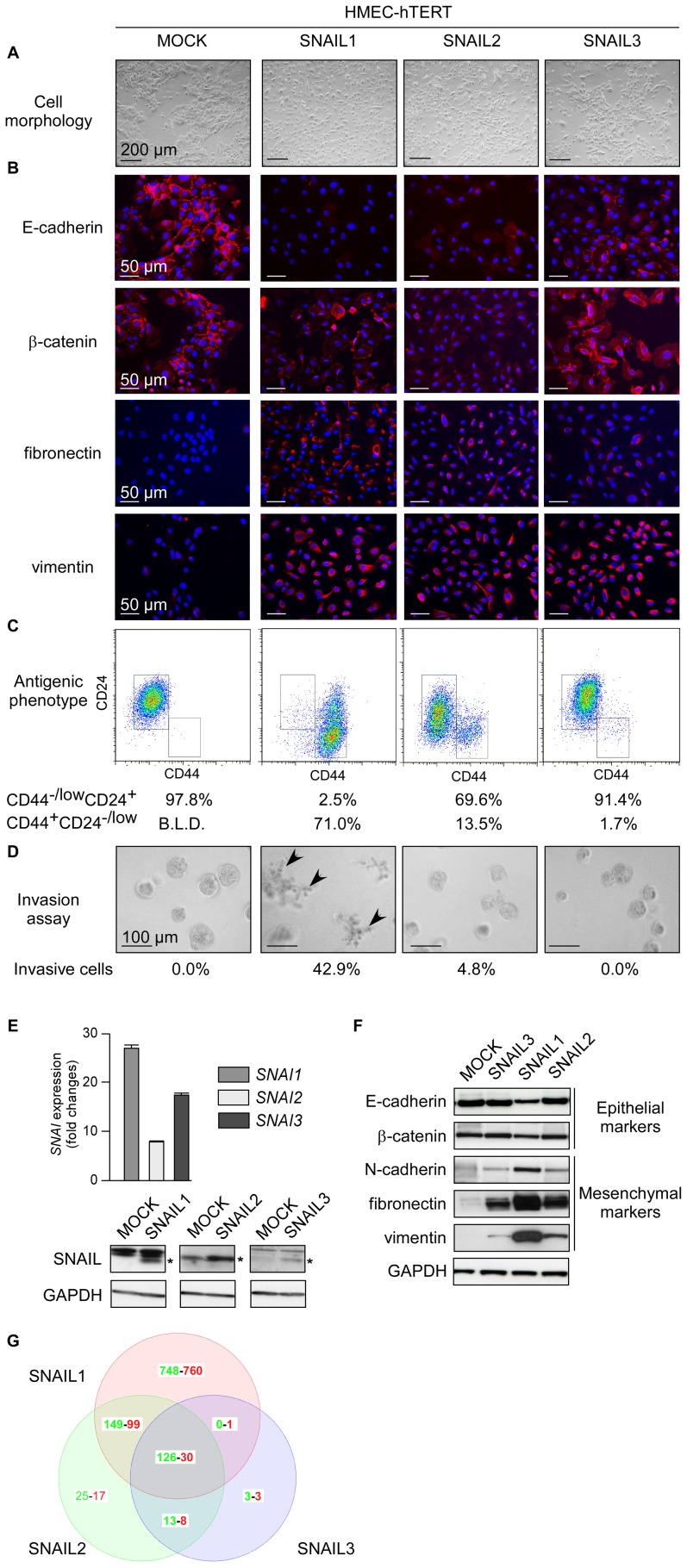
Figure 2. SNAIL proteins act with different potency to promote human mammary epithelial cell commitment into EMT.
HMECs were infected with the SNAI retroviral constructs as indicated at the top. (A) Representative photomicrographs of cells obtained by phase contrast microscopy. (B) Analysis of epithelial markers (E-cadherin, β-catenin) and mesenchymal markers (fibronectin, vimentin) by immunofluorescence. (C) Analysis by flow cytometry of CD44 and CD24. Percentages of CD44−/low CD24+ and CD44+CD24−/low cells are indicated. B.L.D.: below the limit of detection. (D) Invasion assay. Percentages of invasive cells are indicated. Invasive cells are arrowed. (E) Upper panel: Analysis of SNAI-transgene expression by qRT-PCR in the corresponding transfected cell lines. Levels are expressed relatively to the housekeeping gene HPRT1. Lower panels: western blot analysis of SNAIL proteins. Proteins of interest are indicated by stars. (F) Analysis of epithelial and mesenchymal markers by western blotting. (G) Venn diagram showing the overlap of genes upregulated (in red) or down-regulated (in green) in SNAIL-HMEC derivatives as compared to the parental HMEC-hTERT cell line and as determined with a 1.5-fold cut-off and a p value <0.1.