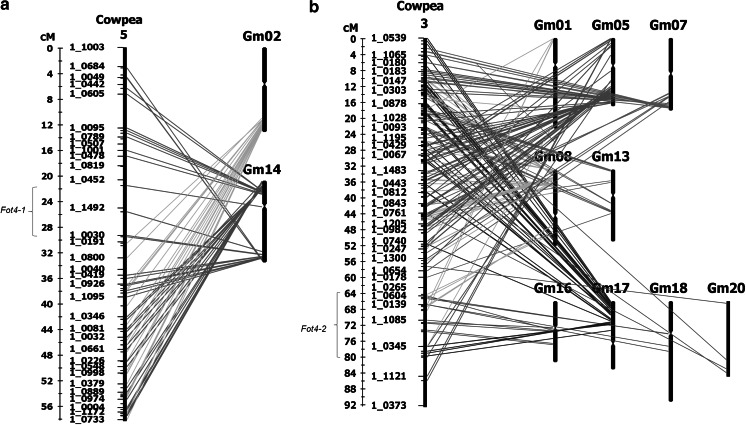
Fig. 3.
a Synteny of Fot4-1 with G. max chromosome 14. Synteny was examined for the Fot4-1 locus between cowpea and G. max using EST-derived SNP markers previously BLASTed and aligned to the sequenced genomes. Fot4-1 spans from 21.57 to 29.40 cM on the cowpea consensus genetic map linkage group 5 and was syntenic at a macro and micro scale with soybean chromosome 14. The Fot4-1 syntenic locus in soybean was identified by soybean orthologs to cowpea SNP markers 1_0557, 1_0662, 1_0986, and 1_0030 and spanned from soybean locus Glyma14g15370 to Glyma14g36620. Three soybean disease-resistance genes, Glyma14g17910, Glyma14g23930, and Glyma14g34880, were observed in the syntenic locus and were considered as orthologous disease-resistance candidate genes for the Fot4-1 locus. Glyma14g17910 and Glyma14g23930 were both annotated as TIR-NBS–LRR genes and Glyma14g34880 was annotated as a leucine-rich repeat protein kinase. b Synteny of Fot4-2 locus with G. max chromosomes 16 and 18. Synteny was examined for the Fot4-2 locus between cowpea and G. max using EST-derived SNP markers previously BLASTed and aligned to the sequenced genomes. The Fot4-2 locus, which spanned 64.44–80.23 cM on cowpea consensus genetic map linkage group 3, was determined to be co-linear with soybean chromosomes 16 and 18. The syntenic region in soybean chromosome 16 spanned from soybean locus Glyma16g15790 to Glyma16g23710, where two soybean disease-resistance genes, Glyma16g17380 and Glyma16g22620, were observed. Glyma16g17380 was annotated as a leucine-rich repeat protein kinase and Glyma16g22620 was annotated as a TIR–NBS–LRR disease-resistance gene. The syntenic Fot4-2 region of soybean chromosome 18 spanned from soybean locus Glyma18g18980 to Glyma18g38670, which corresponded to 65.16–66.99 cM of the Fot4-2 locus. However, the syntenic region preceded the most significant region of the Fot4-2 locus, and no candidate genes were observed