Figure 4.
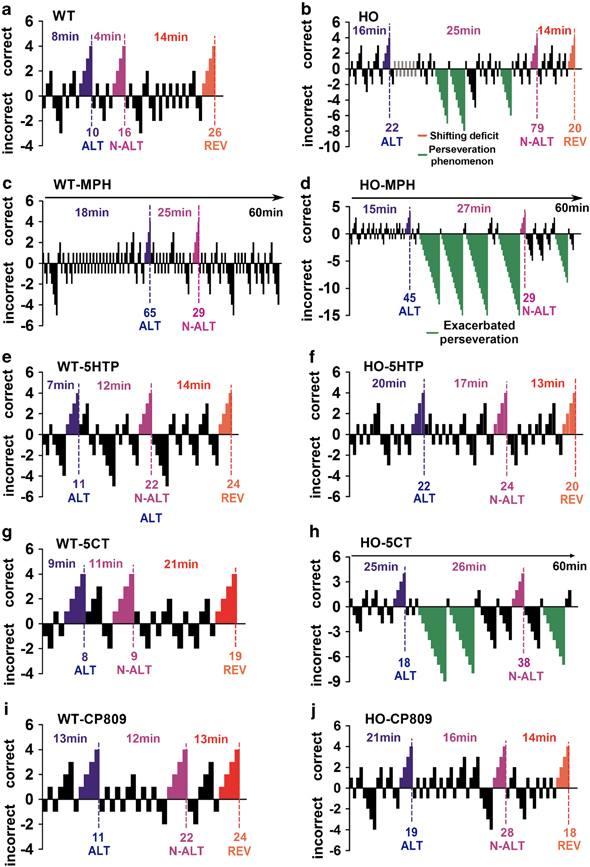
Representative example of the effects of monoaminergic drugs on cognitive performances of Tph2-KI mice. (a and b) Vehicle-treated WT (a) and HO (b) mice. (c and d) MPH-treated WT (c) and HO (d) mice. (e and f) 5-HTP-treated WT (e) and HO (f) mice. (g and h) 5-CT-treated WT (g) and HO (h) mice. (i and j) CP809.101-treated WT (i) and HO (j) mice. Each positive (top) and negative (bottom) bar corresponds to a rewarded or a failed trial, respectively. Dotted lines indicate that the mouse has reached the criterion of four consecutive successful trials for the task as defined (Del'Guidice et al, 2009). Expected correct behaviors are indicated above each task (ALT: blue; N-ALT: purple; REV: red, see Supplementary Figure S1A for details). Numbers on top of each task indicate the time required for the mouse to complete the task. Numbers on the bottom part indicate the number of trials required to complete each task. Shifting deficits (orange bars) and perseveration errors (green bars) are indicated. Shifting deficits were defined as maintenance of the ALT strategy at the beginning of the N-ALT task (see Supplementary Figure S1B for details). Perseveration errors were defined as episodes of more than six repetitive failed attempts as described (Del'Guidice et al, 2009). See method section for a description of drug administration conditions and doses. n=8 mice per conditions, detailed gender repartition and effectives of mice used for the different automated H-Maze experiments are listed in Supplementary Table S2. Relative affinity of 5-CT and CP809.101 for different 5-HT receptors is listed in Supplementary Table S3.
