Figure 5.
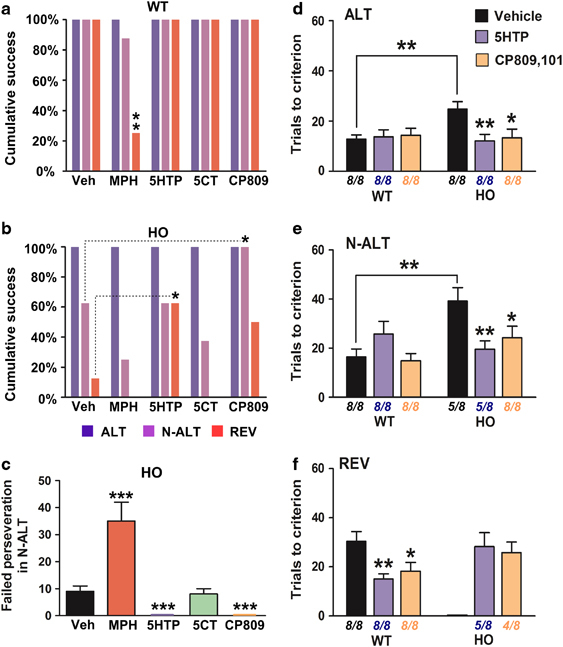
Effects of monoaminergic drug treatment on cumulative success rates, perseveration, and task performances in the automated H-maze. (a and b) Cumulative success rates (%) for WT (a) and HO (b) Tph2-KI mice in all three tasks of the automated H-maze following treatment with: vehicle, MPH, 5-HTP, 5-CT, or CP809.101. See method section for a description of drug administration conditions and doses. Data are presented as % of animals from each initial group that succeeded in completing each tasks. Initial n=8 mice per group. (c) Average number (±SEM) of perseveration errors for HO Tph2-KI mice during the N-ALT task. Perseveration errors were defined as episodes of more than six repetitive failed attempts as defined (Del'Guidice et al, 2009). Calculation of perseveration errors included all animals independently of their ability to complete the N-ALT task. n=8 animals per group. (d–f) Average number of trials (±SEM) required for reaching the criterion of 4 consecutive successful trials for mice of the WT and HO genotype after treatment with vehicle, 5-HTP or CP809.101. See method section for a description of drug administration conditions and doses. (d) the ALT task, (e) the N-ALT task, and (f) the REV task. Average number of trials was calculated only from the performances of mice that completed each task. Initial n=8 mice per genotype, number of remaining animals used to calculate average numbers of trials are indicated below each condition. *p⩽0.05, **p⩽0.01, and ***p⩽0.001, a and b, Mann–Whitney test; c, one-way ANOVA test with Newman–Keuls post hoc test, d–f, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests; f, one-way ANOVA test with Newman–Keuls post hoc test.
